|
|
|
When blood is deoxygenated and flowing back to the heart through the veins, it is dark reddish-blue in color. Blood in the arteries that is oxygenated and flowing out to the body is bright red. Whereas arterial blood comes out in spurts, venous blood flows.
During the twentieth century, a variant of the metric system was used in Russia and France in which the base unit of mass was the tonne. Instead of kilograms, this system used millitonnes (mt).
The human body produces and destroys 15 million blood cells every second.
Hyperthyroidism leads to an increased rate of metabolism and affects about 1% of women but only 0.1% of men. For most people, this increased metabolic rate causes the thyroid gland to become enlarged (known as a goiter).
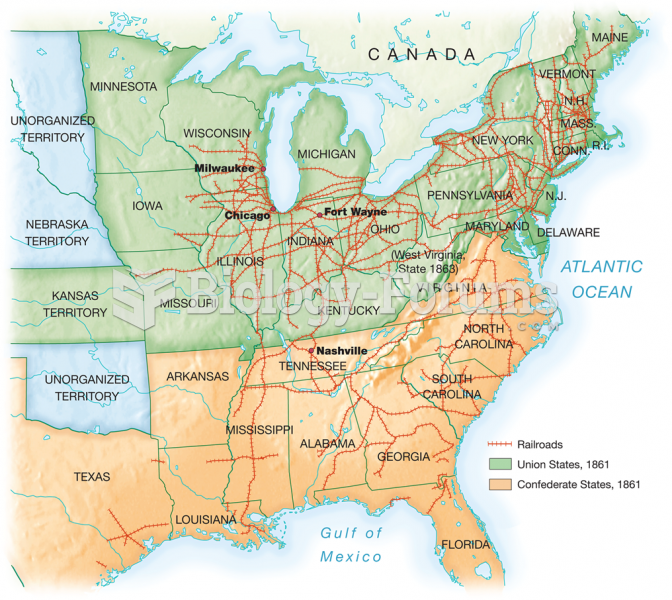
Russia has the highest death rate from cardiovascular disease followed by the Ukraine, Romania, Hungary, and Poland.
 Bow shock formed by the magnetosphere of LL Orionis (center) as it collides with the Orion Nebula fl
Bow shock formed by the magnetosphere of LL Orionis (center) as it collides with the Orion Nebula fl
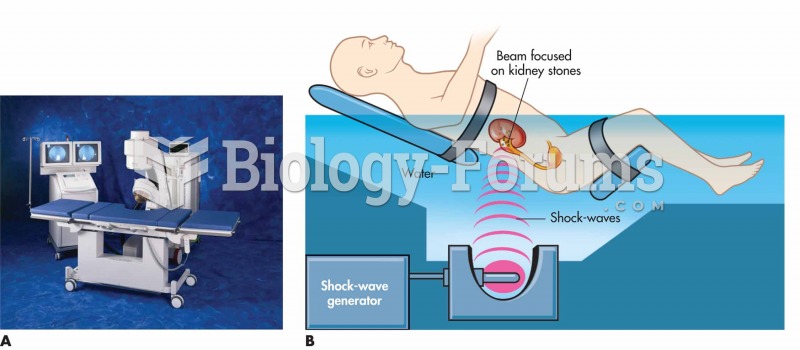 (A) Dornier Compact Delta® lithotripsy system. Acoustic shock waves generated by the shock-wave-gene
(A) Dornier Compact Delta® lithotripsy system. Acoustic shock waves generated by the shock-wave-gene
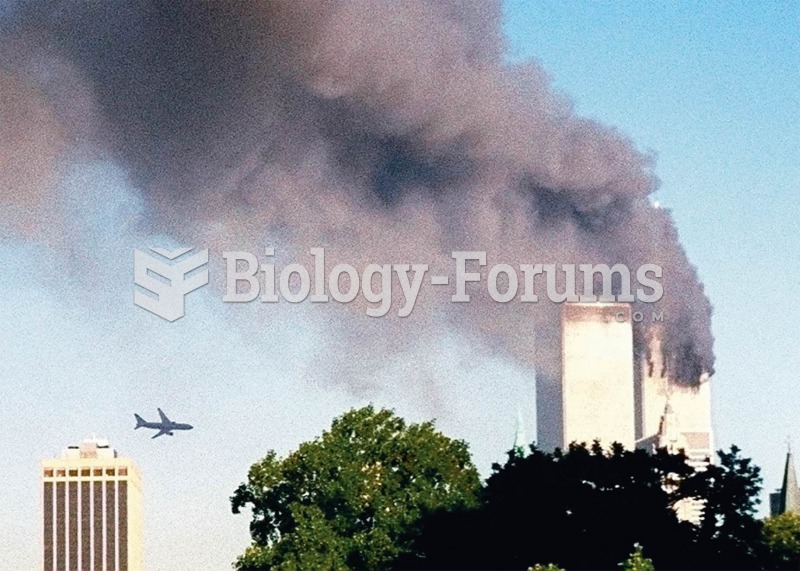 A second jetliner approaches the south tower of the World Trade Center on September 11, 2001. The no
A second jetliner approaches the south tower of the World Trade Center on September 11, 2001. The no