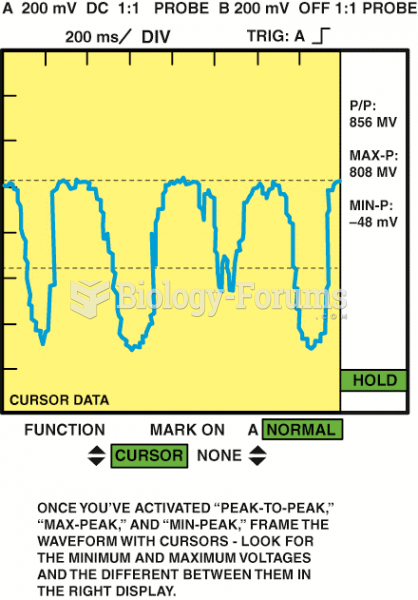
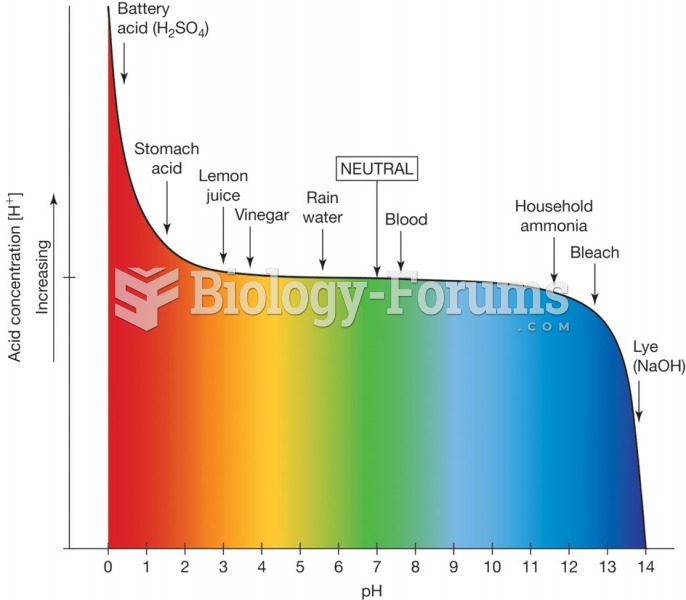
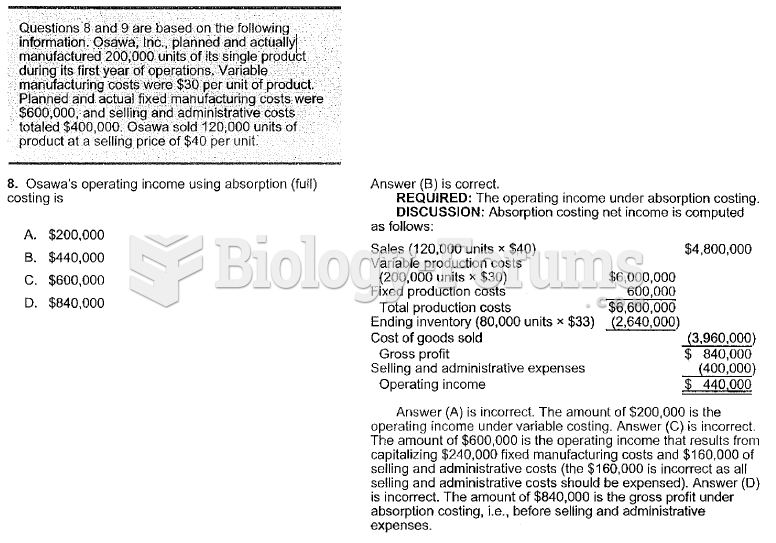
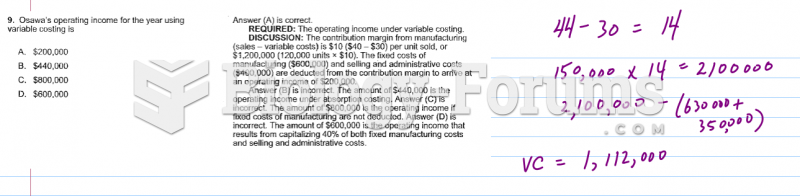
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
There are 20 feet of blood vessels in each square inch of human skin.
Did you know?
A seasonal flu vaccine is the best way to reduce the chances you will get seasonal influenza and spread it to others.
Did you know?
Street names for barbiturates include reds, red devils, yellow jackets, blue heavens, Christmas trees, and rainbows. They are commonly referred to as downers.
Did you know?
After 5 years of being diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, one every three patients will no longer be able to work.
Did you know?
The term pharmacology is derived from the Greek words pharmakon("claim, medicine, poison, or remedy") and logos ("study").