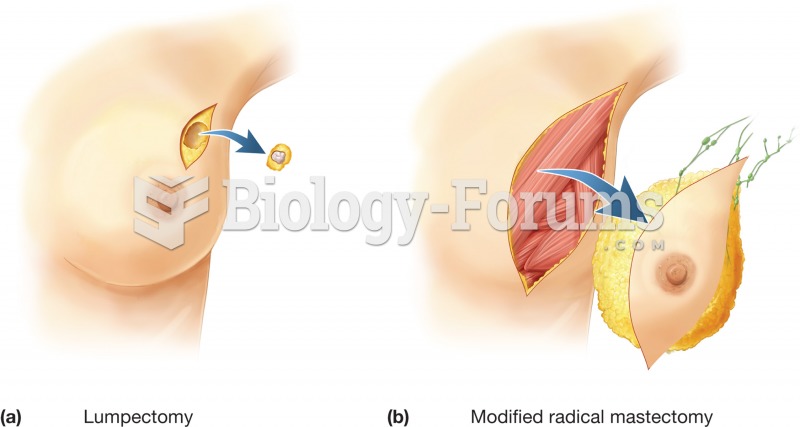
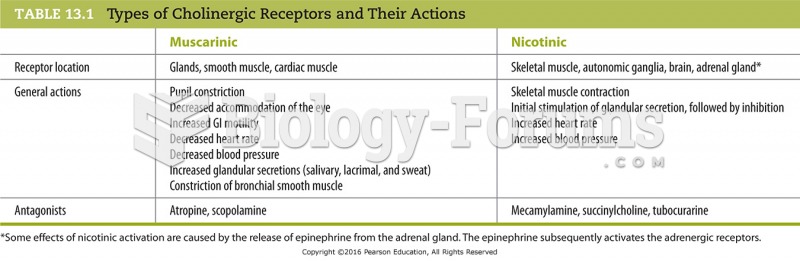
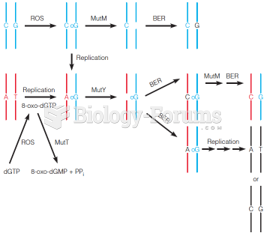
Answer to Question 1
a
Answer to Question 2
Lawyers occupy an ambiguous position in American society. They are admired and respected and at the same time distrusted. Discussions of good lawyers and bad lawyers invariably focus on legal ethics. More so than the other lawyers in the criminal justice process, defense attorneys are most often identified as having ethical issues. Defending unpopular clients is the basis for a great deal of criticism of lawyers. At the core of legal ethics is the notion that every party is entitled to legal representation, even unpopular defendants who have committed heinous crimes or defendants whose guilt is overwhelming. Each state has adopted its own code of professional responsibility for lawyers licensed within it. All 50 U.S. states, however, have adopted some variation of the American Bar Association's Model Rules of Professional Conduct. These rules impose ethical obligations on lawyers to their clients, as well as to the courts since all attorneys are officers of the court.
The duty of candor to the tribunal is the most important responsibilities that all lawyers owe to the courts. This ethical rule prohibits lawyers from knowingly making false statements to the court, failing to disclose adverse legal precedents, obstructing access to or tampering with witnesses or evidence, making frivolous discovery requests, and offering any evidence known to be falseincluding perjurious or misleading testimony. Another key responsibility all lawyers owe to the court, including prosecutors and criminal defense attorneys, is refraining from making any out-of-court statements that an attorney knows or reasonably should know will be disseminated to the public that would have a substantial likelihood of prejudicing any judicial proceeding. The duties that defense attorneys owe to their clients include: zealously representing the client's interests within the bounds of the law;
abiding by a client's decisions concerning the objectives of representation; avoiding providing any counsel that would encourage or assist a client, in conduct that the lawyer knows is criminal or fraudulent; acting with reasonable diligence and promptness in representing a client; keeping the client reasonably informed about the status of his or her case; maintaining client confidentiality; avoiding conflicts of interest. The duty of zealous advocacy formulates the bedrock of legal ethics. Lawyers are expected to be diligent in asserting valid defenses for their clients. Confidentiality is another key component of legal ethics. Potential conflict of interest is a key ethical issue facing lawyers. Lawyers who fail to properly represent their clients may be sued for civil damages (Chapter 2). It is important to stress, though, that lawyers are liable only in very limited situations. Just because a lawyer loses a case does not mean that the lawyer is incompetent.