|
|
|
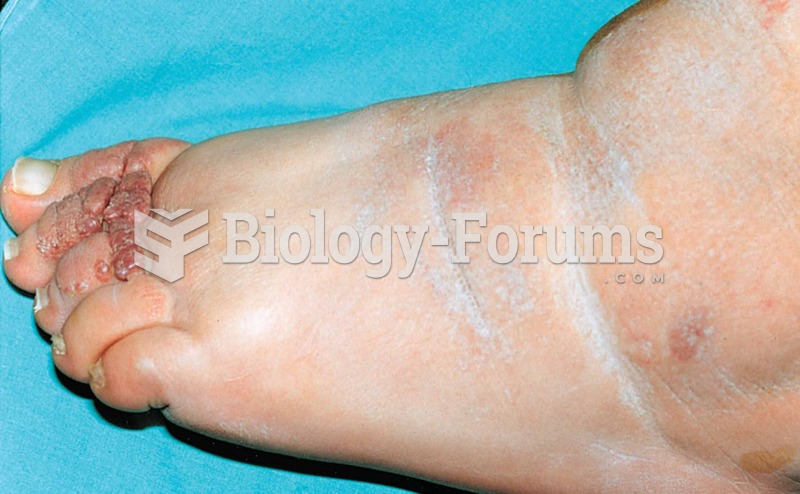
Adult head lice are gray, about ? inch long, and often have a tiny dot on their backs. A female can lay between 50 and 150 eggs within the several weeks that she is alive. They feed on human blood.
Thyroid conditions cause a higher risk of fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome.
In the ancient and medieval periods, dysentery killed about ? of all babies before they reach 12 months of age. The disease was transferred through contaminated drinking water, because there was no way to adequately dispose of sewage, which contaminated the water.
During the twentieth century, a variant of the metric system was used in Russia and France in which the base unit of mass was the tonne. Instead of kilograms, this system used millitonnes (mt).
Alcohol acts as a diuretic. Eight ounces of water is needed to metabolize just 1 ounce of alcohol.