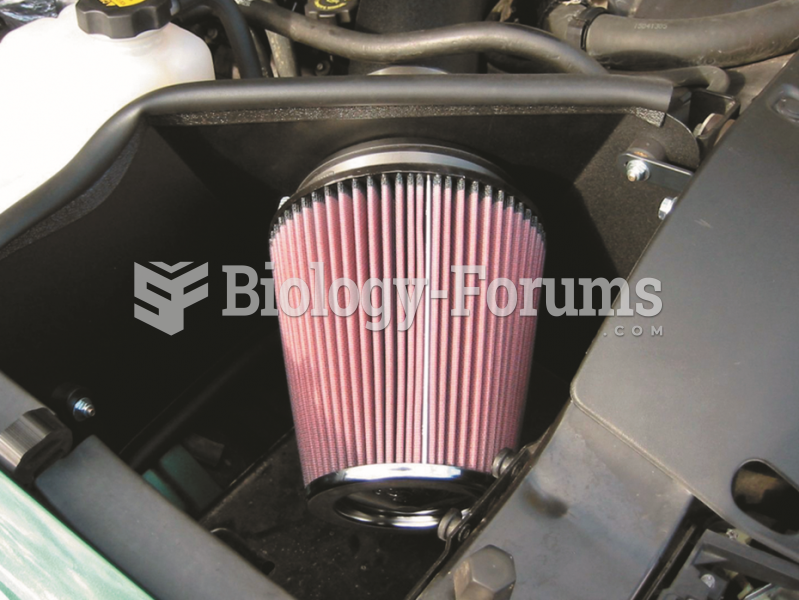
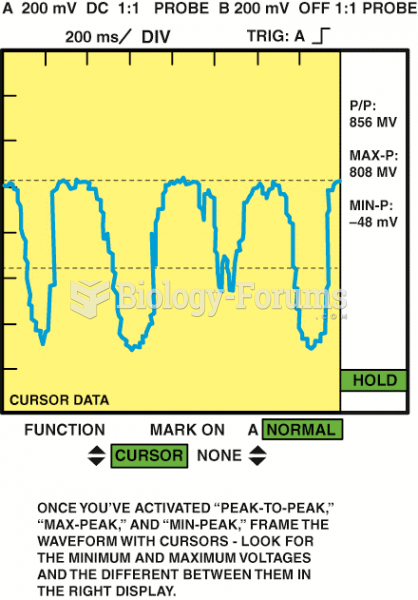
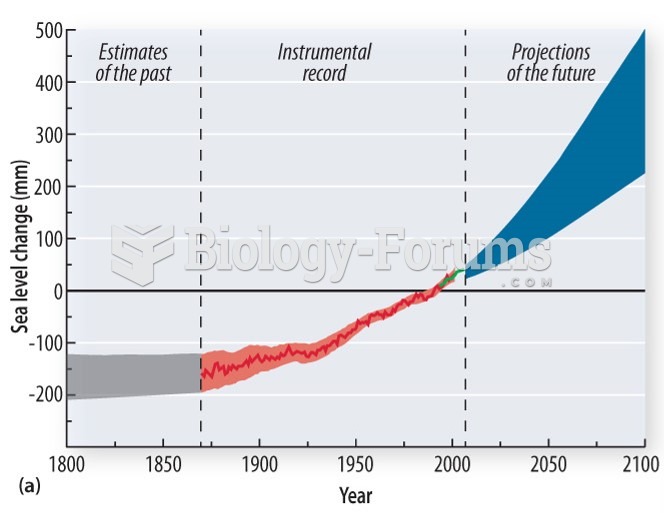
|
|
|
More than 2,500 barbiturates have been synthesized. At the height of their popularity, about 50 were marketed for human use.
Many people have small pouches in their colons that bulge outward through weak spots. Each pouch is called a diverticulum. About 10% of Americans older than age 40 years have diverticulosis, which, when the pouches become infected or inflamed, is called diverticulitis. The main cause of diverticular disease is a low-fiber diet.
In the ancient and medieval periods, dysentery killed about ? of all babies before they reach 12 months of age. The disease was transferred through contaminated drinking water, because there was no way to adequately dispose of sewage, which contaminated the water.
Of the estimated 2 million heroin users in the United States, 600,000–800,000 are considered hardcore addicts. Heroin addiction is considered to be one of the hardest addictions to recover from.
This year, an estimated 1.4 million Americans will have a new or recurrent heart attack.
 A visual inspection on this battery showed that the electrolyte level was below the plates in all ...
A visual inspection on this battery showed that the electrolyte level was below the plates in all ...
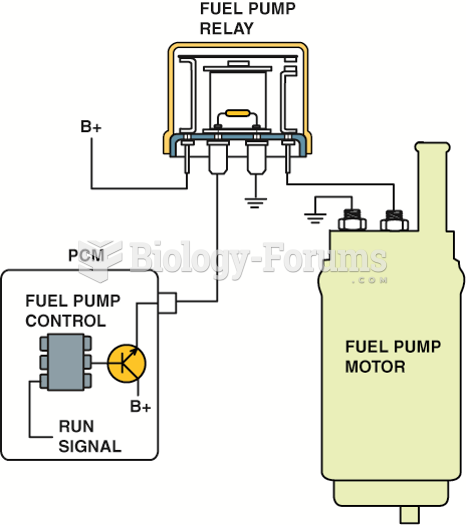 A typical module-controlled high-side driver (HSD) where the module itself supplies the electrical ...
A typical module-controlled high-side driver (HSD) where the module itself supplies the electrical ...