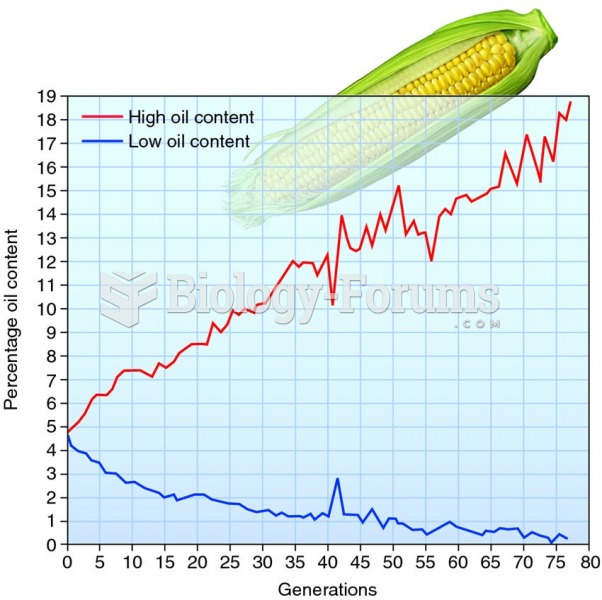
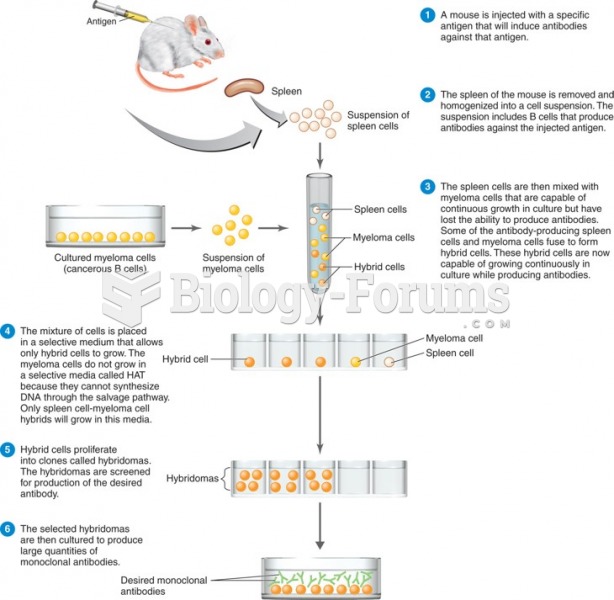
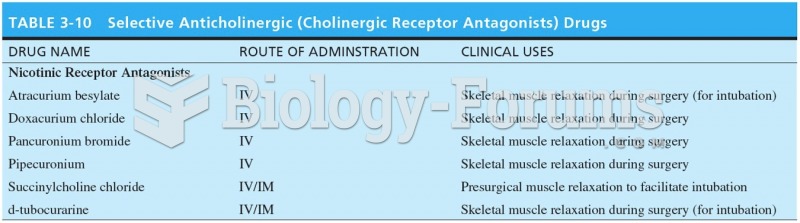
|
|
|
Nitroglycerin is used to alleviate various heart-related conditions, and it is also the chief component of dynamite (but mixed in a solid clay base to stabilize it).
Vaccines prevent between 2.5 and 4 million deaths every year.
Elderly adults are living longer, and causes of death are shifting. At the same time, autopsy rates are at or near their lowest in history.
Pubic lice (crabs) are usually spread through sexual contact. You cannot catch them by using a public toilet.
Drug abusers experience the following scenario: The pleasure given by their drug (or drugs) of choice is so strong that it is difficult to eradicate even after years of staying away from the substances involved. Certain triggers may cause a drug abuser to relapse. Research shows that long-term drug abuse results in significant changes in brain function that persist long after an individual stops using drugs. It is most important to realize that the same is true of not just illegal substances but alcohol and tobacco as well.
 When the United States gets stuck over a controversial issue—usually something a divided Congress ca
When the United States gets stuck over a controversial issue—usually something a divided Congress ca
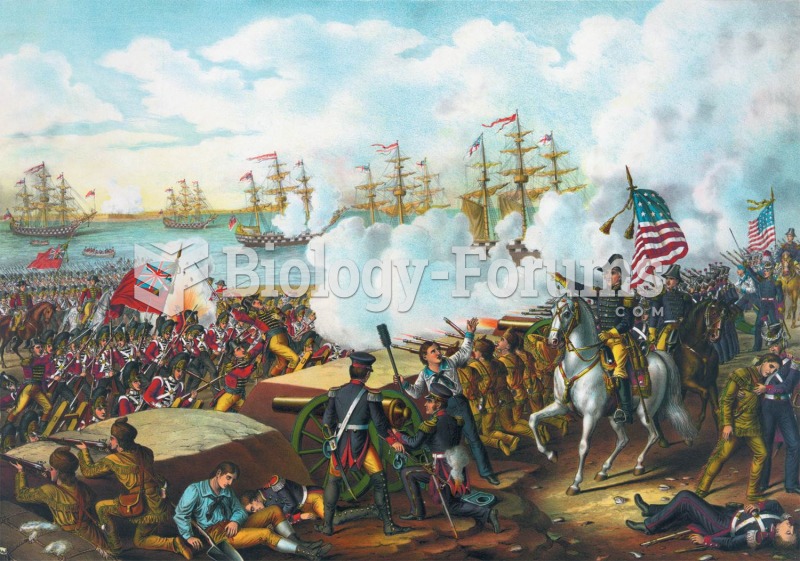 General Andrew Jackson, on the horse, exhorts his men to throw back the advancing British; they succ
General Andrew Jackson, on the horse, exhorts his men to throw back the advancing British; they succ