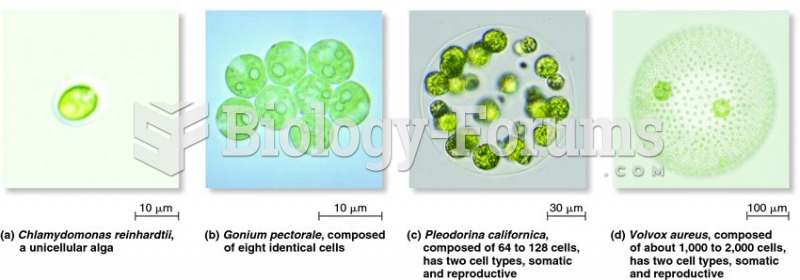
|
|
|
Nitroglycerin is used to alleviate various heart-related conditions, and it is also the chief component of dynamite (but mixed in a solid clay base to stabilize it).
Signs of depression include feeling sad most of the time for 2 weeks or longer; loss of interest in things normally enjoyed; lack of energy; sleep and appetite disturbances; weight changes; feelings of hopelessness, helplessness, or worthlessness; an inability to make decisions; and thoughts of death and suicide.
In the United States, there is a birth every 8 seconds, according to the U.S. Census Bureau's Population Clock.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved Risperdal, an adult antipsychotic drug, for the symptomatic treatment of irritability in children and adolescents with autism. The approval is the first for the use of a drug to treat behaviors associated with autism in children. These behaviors are included under the general heading of irritability and include aggression, deliberate self-injury, and temper tantrums.
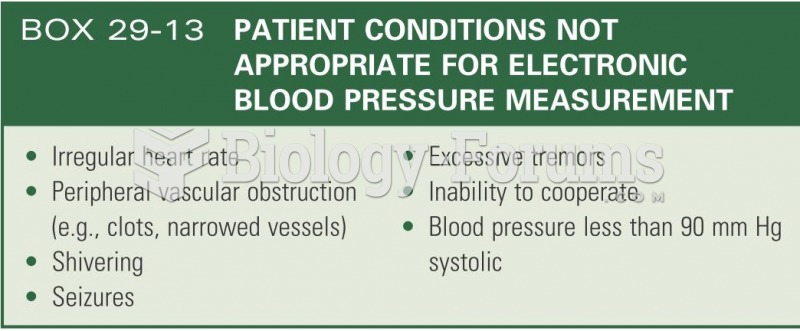
All adverse reactions are commonly charted in red ink in the patient's record and usually are noted on the front of the chart. Failure to follow correct documentation procedures may result in malpractice lawsuits.
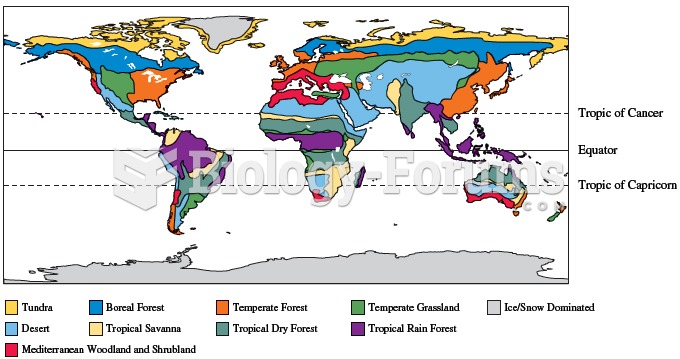 Variation in climatic conditions result in geographic variation in the distribution of biome types a
Variation in climatic conditions result in geographic variation in the distribution of biome types a
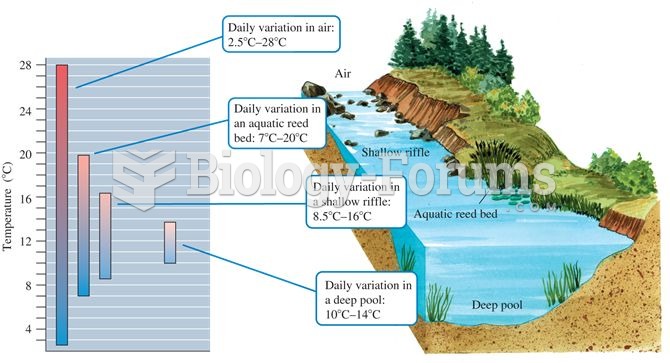 Aquatic microclimates: aquatic environments generally show less temperature variation compared to te
Aquatic microclimates: aquatic environments generally show less temperature variation compared to te