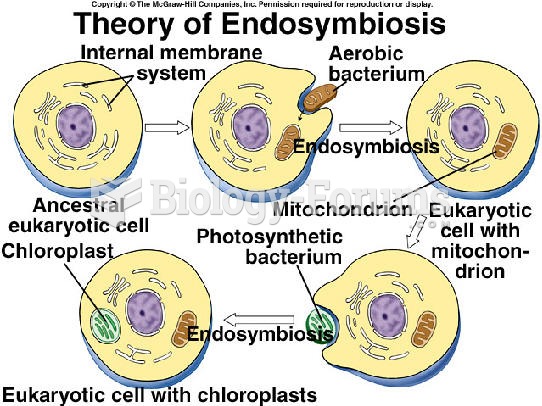
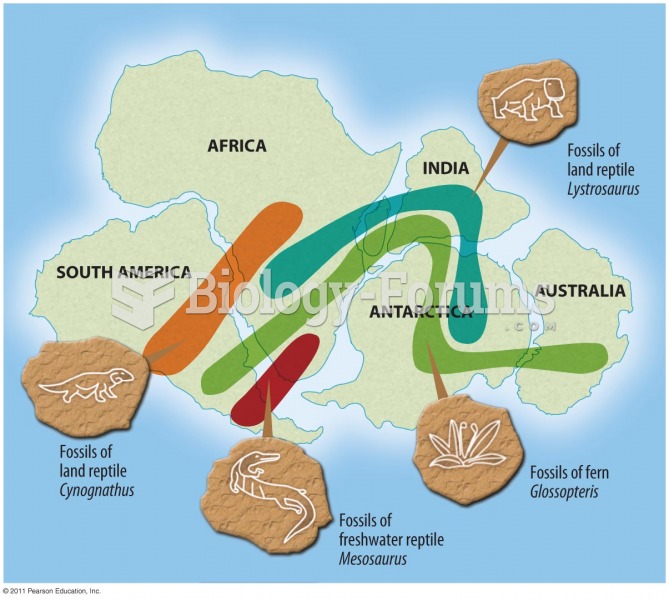
Answer to Question 1Alfred Wegener's theory of continental drift was proposed in 1912. This theory maintained that all the continents were once connected into a single continent. Wegener called this large continent Pangaea and the surrounding ocean Panthalassa. He thought that Pangaea began to break into continents about 200 million years ago. Wegener used the shape of the continents from the north and south Atlantic to show how the continents would have fit together. There was also an alignment of mountain ranges of similar age, composition, and structure on different continents. Sir Ernest Shackleton discovered coal in Antarctica which meant that at some point there were tropical plants where it is now freezing. This added to Wegener's evidence of continental drift. There were similar fossils found on different continents. Wegener proposed that the continents moved due to a combination of the centrifugal effect of being slung towards the equator and tidal drag. Wegner lost credibility among scientists by selecting only the data that would support his theory and ignoring contrary data. There were holes in his theory, including a lack of evidence on the floor of the ocean that continents had moved.
Answer to Question 2ANS:Answer
should include:
Seafloor spreading involves the creation of new crust and the destruction of old crust.
Spreading centers occur where there is formation of new crust rising from the
asthenosphere. The ocean floor is thinner in these areas. As the crust cools and moves
away from the centers it becomes cool and denser.
The discovery of subduction zones enhanced the credibility of the seafloor spreading and
plate tectonics theories. Subduction zones are areas where crust plunges back down into
the mantle.
Plate tectonics involves the movement of different lithospheric plates across the
asthenosphere. These plates can be outlined by volcanic activities and mountain ranges.
They move by two forces. When crust forms at the spreading centers it then slides off
the raised ridges. The second force occurs when the crust is pulled downward into the
mantle by the cool, dense leading edge.
Seafloor spreading and plate tectonics built upon Alfred Wegener's previous theory of
continental drift by explaining the driving force of the movement of the continents.