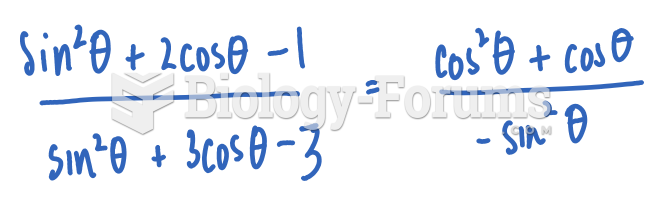Write an equation for the reaction of boron trifluoride, an important reagent in organic chemistry, with trimethylamine. Represent the movement of electrons with a curved arrow, and show the formal charges on the atoms in the product.
 Question 2
Question 2Use the curved arrow method to show the electron movement, and label the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base.
 Question 3
Question 3Identify the reactants and product in the reaction below as acids or bases and specify whether they are Lewis and/or Brnsted-Lowry.


 Question 4
Question 4Which is the strongest base (p
Ka values given for conjugate acid)?
a.
NH
3 (p
Ka = 9.2)
b.
CH
3O
- (p
Ka = 16)
c.

(p
Ka = -6.5)
d.
CH
3CO
2- (p
Ka = 4.7)
e.
H
- (p
Ka = 35)
Question 5Draw a Lewis structure for each of the following.
a)
hydroxylammonium ion:
+NH
3OH.
b)
azide ion: (N
3-)
Question 6Of the bonds found in

which is the most polar?
a.
C-F
b.
O-H
c.
C-H
d.
C-O
Question 7Instructions: Indole is pleasant smelling in highly dilute solutions and has been used in perfumery. Use the structure of indole, below, to answer the following question(s).

Refer to instructions. Indole can function as a Lewis base in the presence of strong acid. Formulate a reaction, using a generic acid (HA), showing electron flow with arrows, that demonstrates this reactivity of indole.
Question 8Instructions: Indole is pleasant smelling in highly dilute solutions and has been used in perfumery. Use the structure of indole, below, to answer the following question(s).

Refer to instructions. Indole can function as a Brnsted-Lowry acid in the presence of strong bases. Formulate a reaction, using a generic base (:B
-), showing electron flow with arrows, that demonstrates this reactivity of indole.
Question 9Instructions: Consider the reaction below to answer the following question.

Refer to instructions. Using the curved arrow formalism, show the flow of electrons for this reaction.
Question 10Instructions: Consider the species below to answer the following question.
BF
3 Fe
2+ 

Refer to instructions. Which of the following would be common to all?
a.
Lewis acids
b.
Lewis bases
c.
Lewis acids or bases
d.
Neither Lewis acids nor bases
Question 11Circle the Lewis bases in the group of compounds below.
 Question 12
Question 12Instructions: Refer to the following equation to answer the question(s) below.

Refer to instructions. Will this reaction take place as written in the forward direction? Explain.
Question 13Instructions: Refer to the following equation to answer the question(s) below.

Refer to instructions. The strongest Brnsted-Lowry base in the equation is indicated by letter _____.
Question 14Instructions: Refer to the following equation to answer the question(s) below.

Refer to instructions. The strongest Brnsted-Lowry acid in the equation is indicated by letter _____.
Question 15Consider the structure of acetic acid shown below.

In the electrostatic potential map of acetic acid, in which of the following bonds would the terminal atom appear as the deepest shade of red?
a.
C=O
b.
C-H
c.
C-C
d.
O-H
Question 16The following shows an intermediate used in a Grignard synthesis. Which atom will inductively donate electrons in this species?

a.
C
b.
Br
c.
Mg
d.
H
e.
both b and c
Question 17Refer to instructions. A C-O bond in tetrahydrofuran,
 Question 18
Question 18Instructions: Use the convention d-/d+ and the crossed arrow (

) to show the direction of the expected polarity of the indicated bonds in the following compound(s).
Refer to instructions. The C-F bond in fluorobenzene,
 Question 19
Question 19In the two structures shown below, what do the positions labeled with the arrow have in common?

a.
the same type of hybridization on the carbon atom
b.
the same geometry around the carbon atom
c.
the same number of hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbon atom
d.
both carbon atoms are involved in a p bond
Question 20Instructions: Consider the two structures below to answer the following question.
CH
3CH
2OH CH
3OCH
3 Refer to instructions. Which of the following correctly describes the structure of these compounds?
a.
All carbon atoms are
sp3 hybridized.
b.
All of the bonds are sigma bonds.
c.
Each oxygen atom has two nonbonding pairs of electrons.
d.
The bond angle around each oxygen atom is ideally about 109.5.
e.
All of these