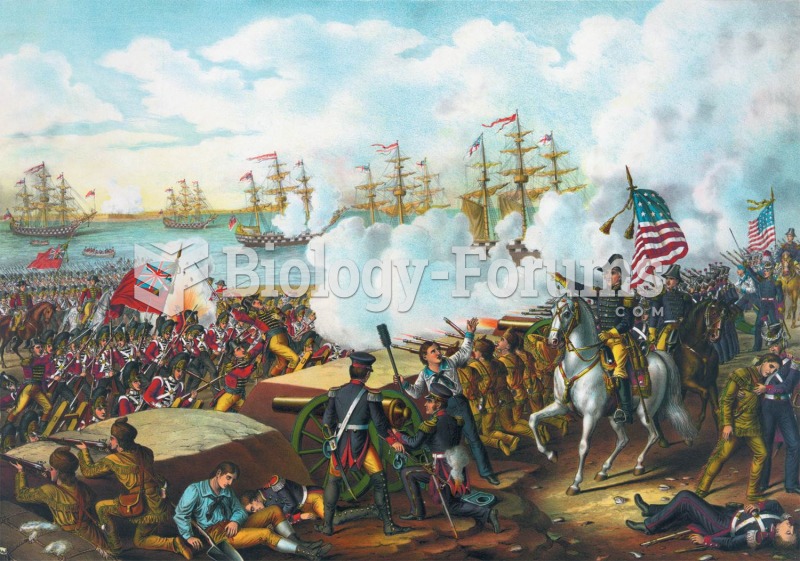
|
|
|
Drug-induced pharmacodynamic effects manifested in older adults include drug-induced renal toxicity, which can be a major factor when these adults are experiencing other kidney problems.
Essential fatty acids have been shown to be effective against ulcers, asthma, dental cavities, and skin disorders such as acne.
The shortest mature adult human of whom there is independent evidence was Gul Mohammed in India. In 1990, he was measured in New Delhi and stood 22.5 inches tall.
The lipid bilayer is made of phospholipids. They are arranged in a double layer because one of their ends is attracted to water while the other is repelled by water.
In 2012, nearly 24 milliion Americans, aged 12 and older, had abused an illicit drug, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA).
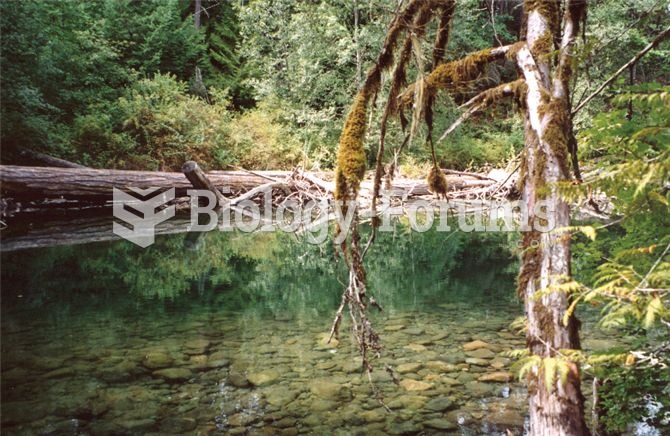 Many salmon spawning grounds, such as the Little Qualicum River in British Columbia, consist of wate
Many salmon spawning grounds, such as the Little Qualicum River in British Columbia, consist of wate
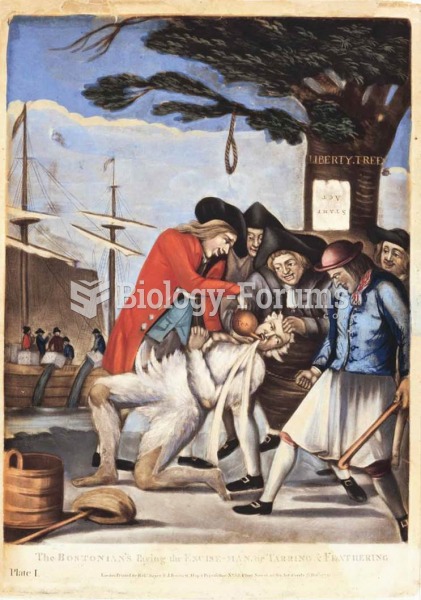 A noose hanging from a “Liberty Tree” reveals this artist’s bias: The “tar-and-feathering” of a Brit
A noose hanging from a “Liberty Tree” reveals this artist’s bias: The “tar-and-feathering” of a Brit