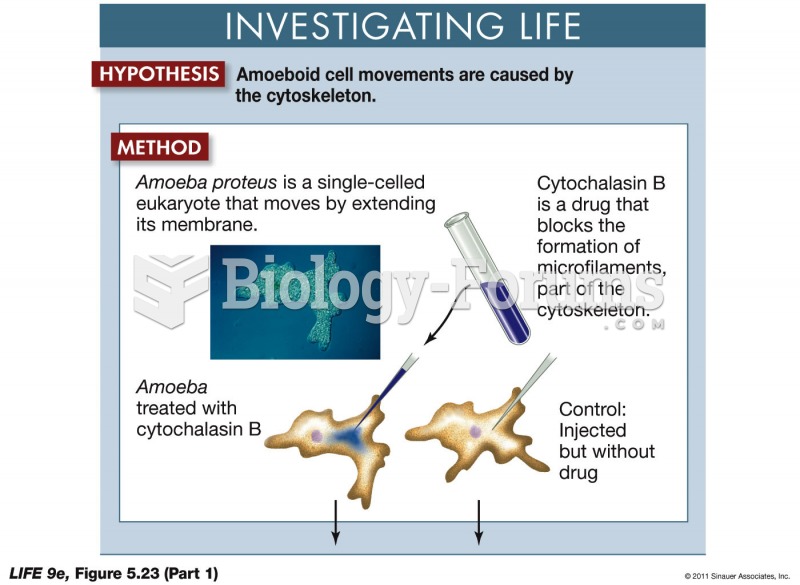
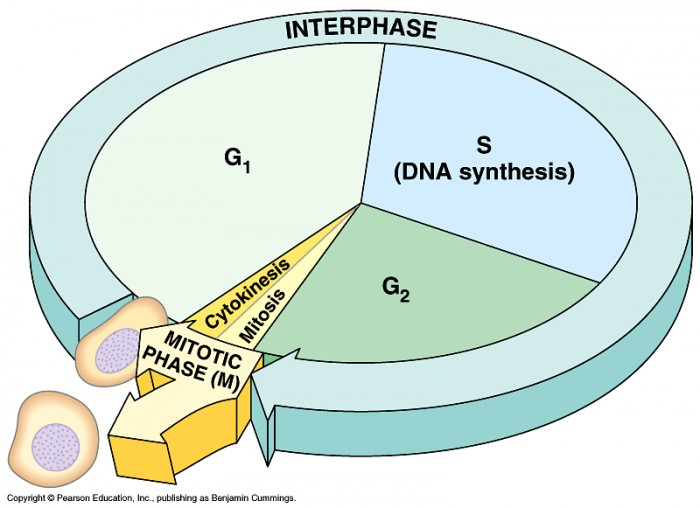
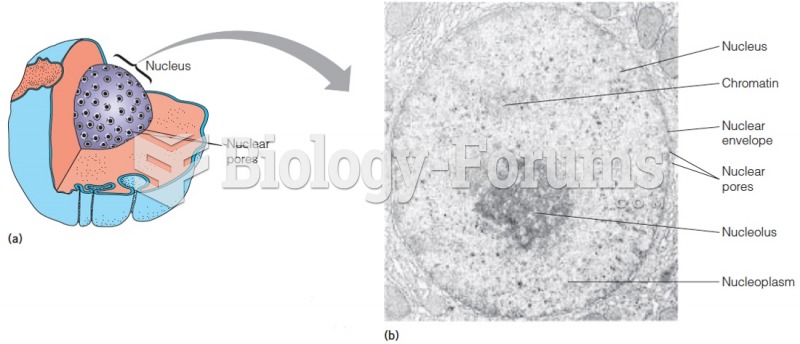
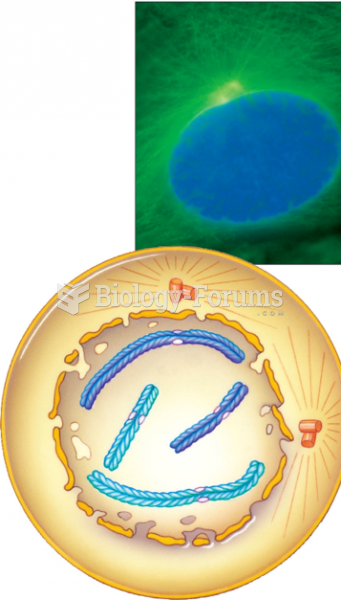
|
|
|
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.
IgA antibodies protect body surfaces exposed to outside foreign substances. IgG antibodies are found in all body fluids. IgM antibodies are the first type of antibody made in response to an infection. IgE antibody levels are often high in people with allergies. IgD antibodies are found in tissues lining the abdomen and chest.
Asthma attacks and symptoms usually get started by specific triggers (such as viruses, allergies, gases, and air particles). You should talk to your doctor about these triggers and find ways to avoid or get rid of them.
Allergies play a major part in the health of children. The most prevalent childhood allergies are milk, egg, soy, wheat, peanuts, tree nuts, and seafood.
Alcohol acts as a diuretic. Eight ounces of water is needed to metabolize just 1 ounce of alcohol.