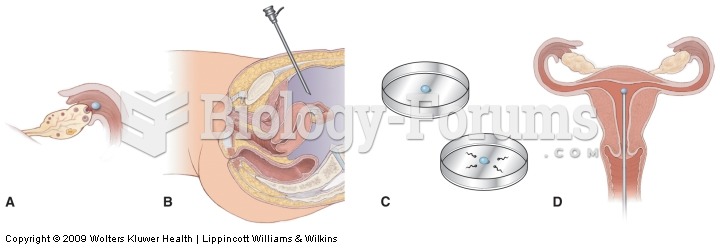
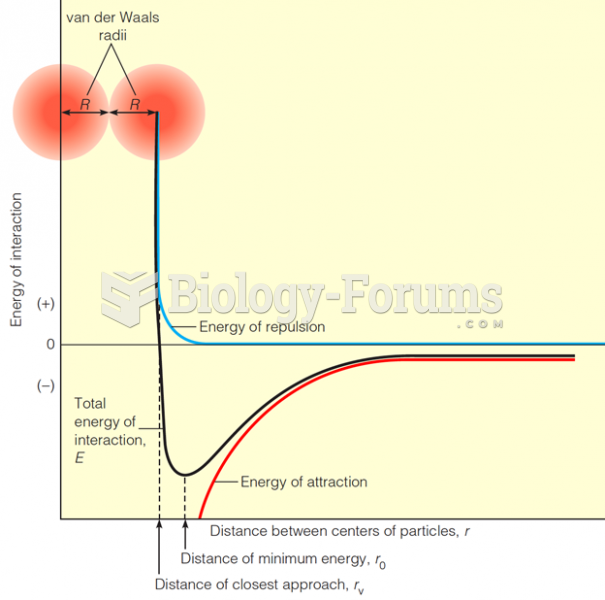
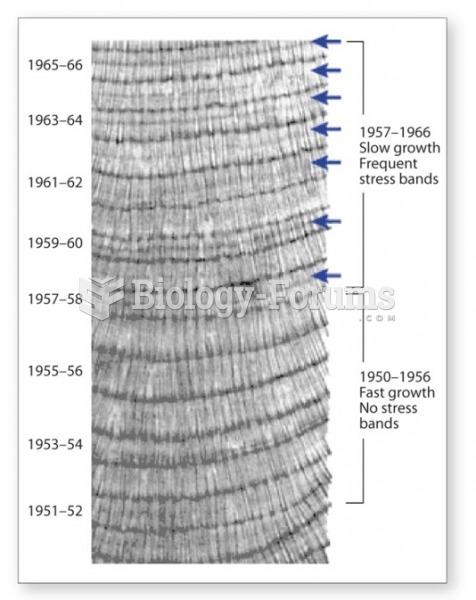
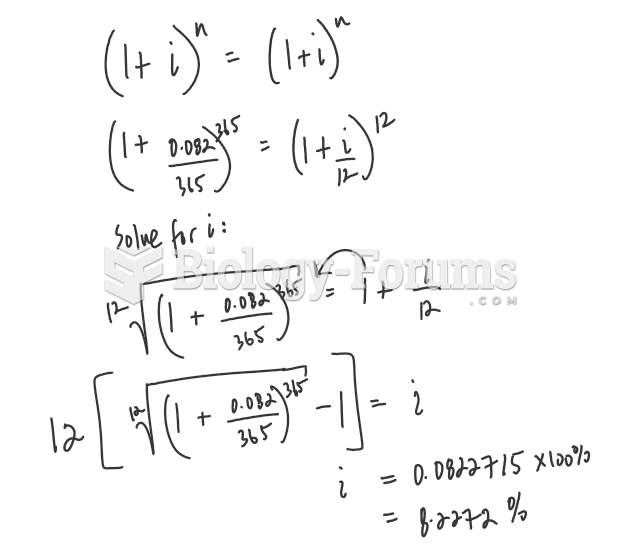This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
More than 30% of American adults, and about 12% of children utilize health care approaches that were developed outside of conventional medicine.
Did you know?
A seasonal flu vaccine is the best way to reduce the chances you will get seasonal influenza and spread it to others.
Did you know?
Alzheimer's disease affects only about 10% of people older than 65 years of age. Most forms of decreased mental function and dementia are caused by disuse (letting the mind get lazy).
Did you know?
The first documented use of surgical anesthesia in the United States was in Connecticut in 1844.
Did you know?
About 100 new prescription or over-the-counter drugs come into the U.S. market every year.