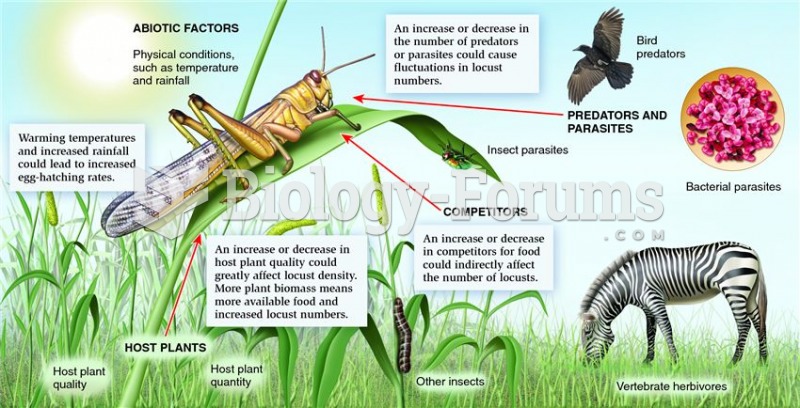
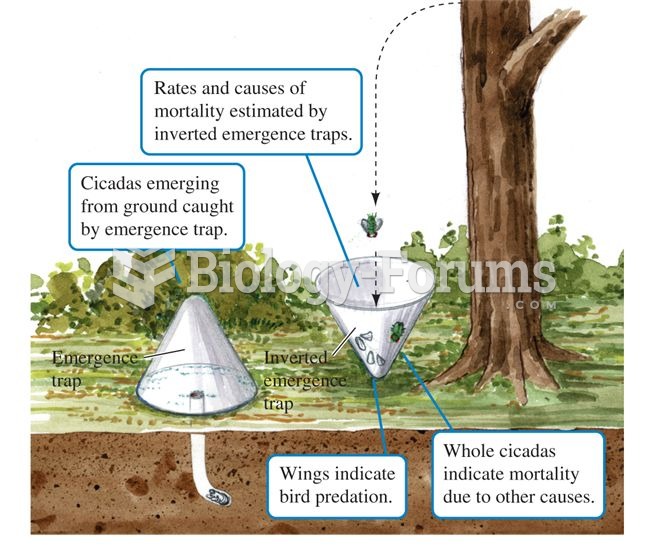
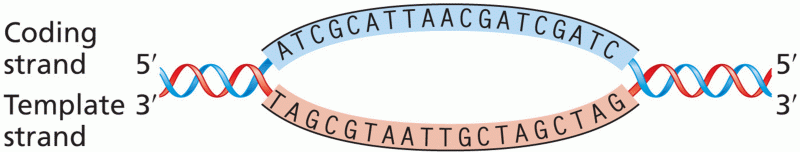
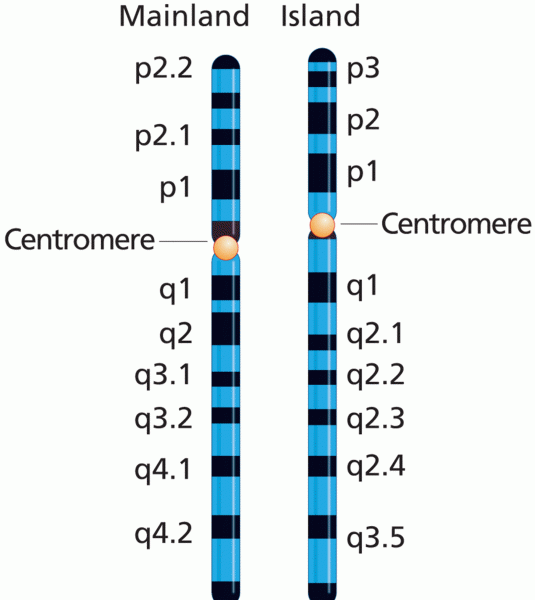
|
|
|
You should not take more than 1,000 mg of vitamin E per day. Doses above this amount increase the risk of bleeding problems that can lead to a stroke.
Blood in the urine can be a sign of a kidney stone, glomerulonephritis, or other kidney problems.
Persons who overdose with cardiac glycosides have a better chance of overall survival if they can survive the first 24 hours after the overdose.
Most childhood vaccines are 90–99% effective in preventing disease. Side effects are rarely serious.
An identified risk factor for osteoporosis is the intake of excessive amounts of vitamin A. Dietary intake of approximately double the recommended daily amount of vitamin A, by women, has been shown to reduce bone mineral density and increase the chances for hip fractures compared with women who consumed the recommended daily amount (or less) of vitamin A.