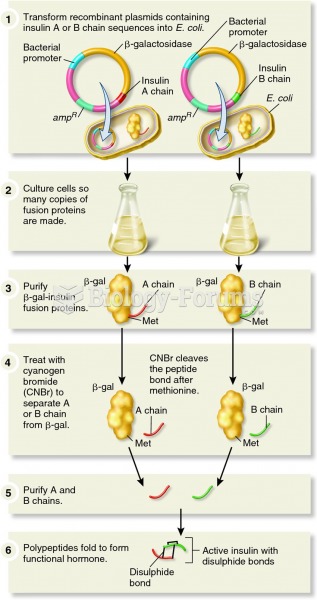
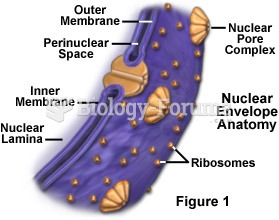
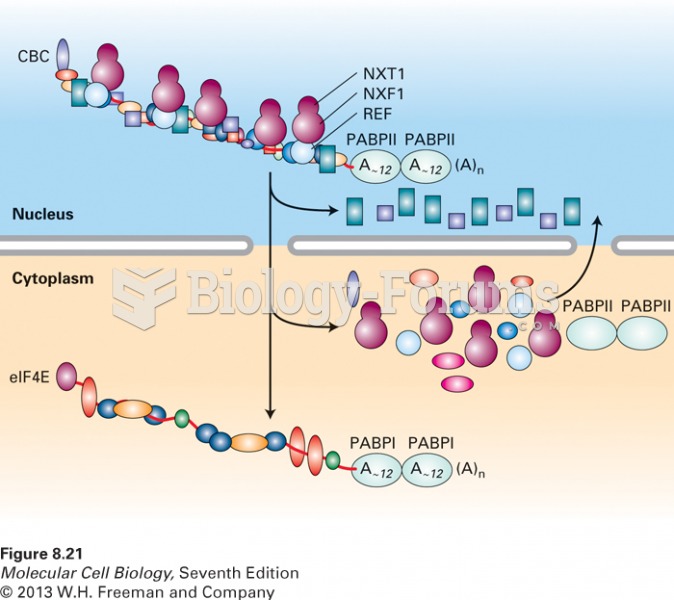
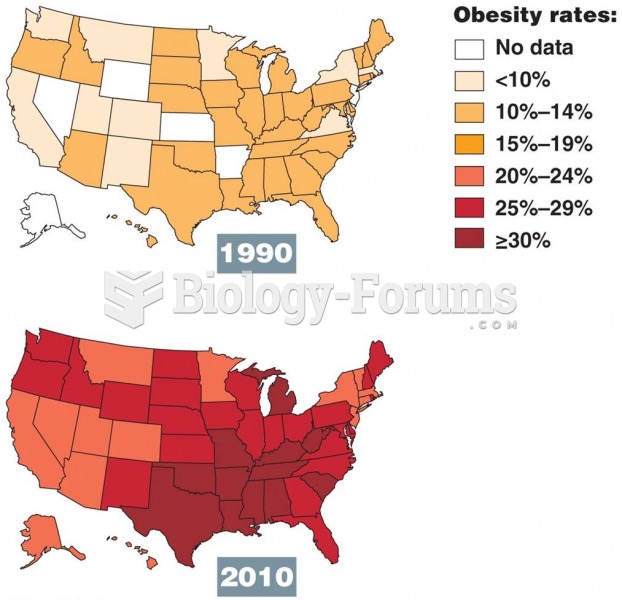
|
|
|
More than 30% of American adults, and about 12% of children utilize health care approaches that were developed outside of conventional medicine.
The top five reasons that children stay home from school are as follows: colds, stomach flu (gastroenteritis), ear infection (otitis media), pink eye (conjunctivitis), and sore throat.
Nearly 31 million adults in America have a total cholesterol level that is more than 240 mg per dL.
The average person is easily confused by the terms pharmaceutics and pharmacology, thinking they are one and the same. Whereas pharmaceutics is the science of preparing and dispensing drugs (otherwise known as the science of pharmacy), pharmacology is the study of medications.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.