Answer to Question 1
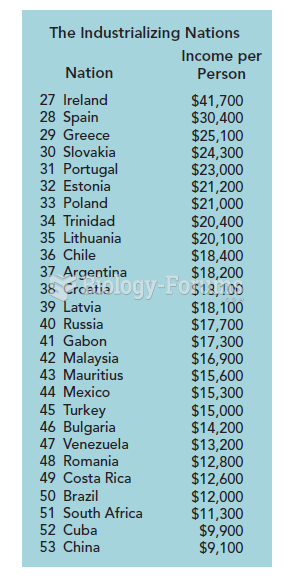
Newly industrialized countries (NICs) are the most prosperous members of the Global
South, which have become important exporters of manufactured goods as well as
important markets for the major industrialized countries that export capital goods.
Export-led industrialization is a growth strategy that concentrates on developing
domestic export industries capable of competing in overseas markets. Importsubstitution industrialization is a strategy for economic development that centers on
providing investors at home incentives to produce goods so that previously imported
products from abroad will decline.
Answer to Question 2
Modernization theory is a view of development popular in the Global North's liberal
democracies that wealth is created through efficient production, free enterprise, and
free trade, and that countries' relative wealth depends on technological innovation and
education more than on natural endowments such as climate and resources.
Dependency theory emphasizes international factors, specifically the Global South's
dependence on the dominant great powers. Its central proposition is that the
structure of the capitalist world economy is based on a division of labor between a
dominant core and a subordinate periphery. As a result of colonialism, the Global
South countries that make up the periphery have been forced into an economic role
whereby they export raw materials and import finished goods. Whereas classical
liberal theorists submit that specialization in production according to comparative
advantage will increase income in an unfettered market and thereby help close the
gap between the world's haves and havenots, dependency theorists maintain that
global inequalities cannot be reduced so long as developing countries continue to
specialize in producing primary products for which there are often numerous
competing suppliers and limited demand.