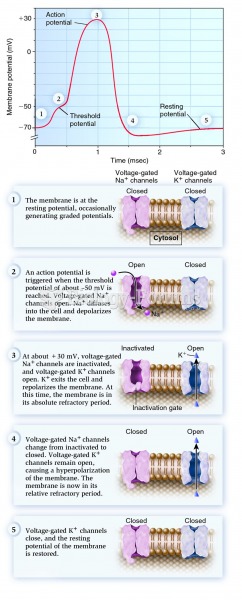
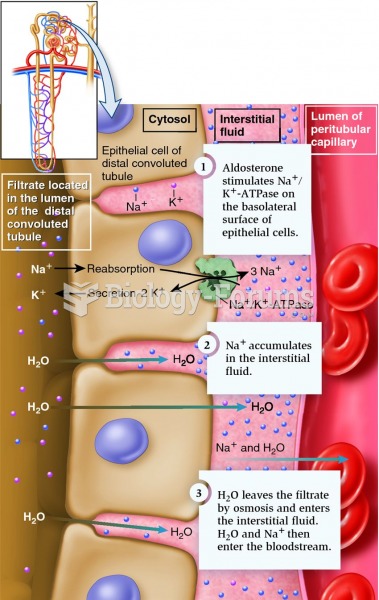
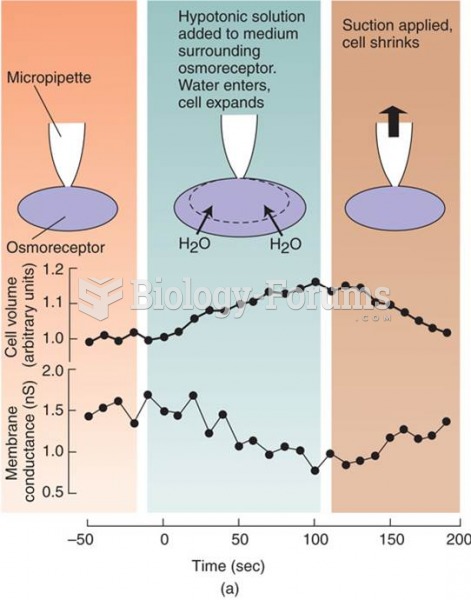
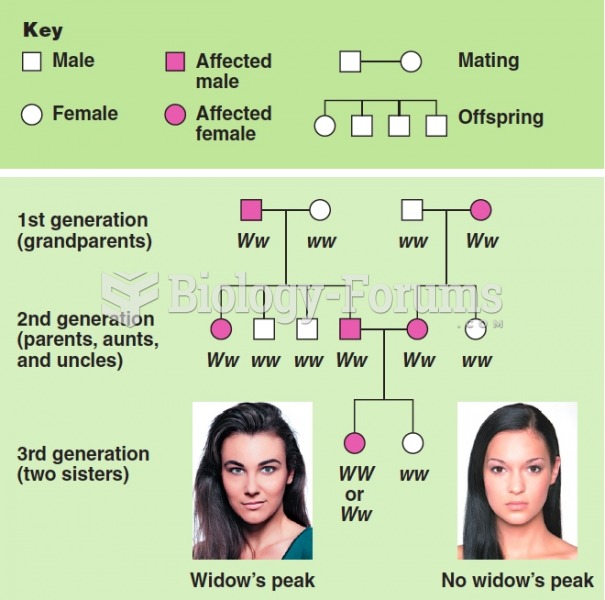
|
|
|
Blood in the urine can be a sign of a kidney stone, glomerulonephritis, or other kidney problems.
Most strokes are caused when blood clots move to a blood vessel in the brain and block blood flow to that area. Thrombolytic therapy can be used to dissolve the clot quickly. If given within 3 hours of the first stroke symptoms, this therapy can help limit stroke damage and disability.
Alcohol acts as a diuretic. Eight ounces of water is needed to metabolize just 1 ounce of alcohol.
Not getting enough sleep can greatly weaken the immune system. Lack of sleep makes you more likely to catch a cold, or more difficult to fight off an infection.
Interferon was scarce and expensive until 1980, when the interferon gene was inserted into bacteria using recombinant DNA technology, allowing for mass cultivation and purification from bacterial cultures.