|
|
|
Drug abusers experience the following scenario: The pleasure given by their drug (or drugs) of choice is so strong that it is difficult to eradicate even after years of staying away from the substances involved. Certain triggers may cause a drug abuser to relapse. Research shows that long-term drug abuse results in significant changes in brain function that persist long after an individual stops using drugs. It is most important to realize that the same is true of not just illegal substances but alcohol and tobacco as well.
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
About one in five American adults and teenagers have had a genital herpes infection—and most of them don't know it. People with genital herpes have at least twice the risk of becoming infected with HIV if exposed to it than those people who do not have genital herpes.
Every 10 seconds, a person in the United States goes to the emergency room complaining of head pain. About 1.2 million visits are for acute migraine attacks.
Cucumber slices relieve headaches by tightening blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the area, and relieving pressure.
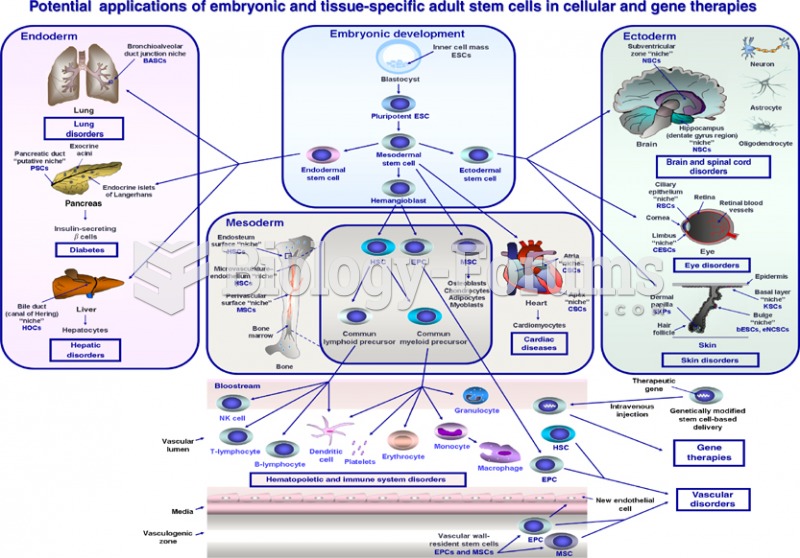 Potential applications of embryonic and tissue specific adult stem cell in cellular and gene theraph
Potential applications of embryonic and tissue specific adult stem cell in cellular and gene theraph
 Material safety data sheets (MSDS), now called safety data sheets (SDS), should be readily available ...
Material safety data sheets (MSDS), now called safety data sheets (SDS), should be readily available ...