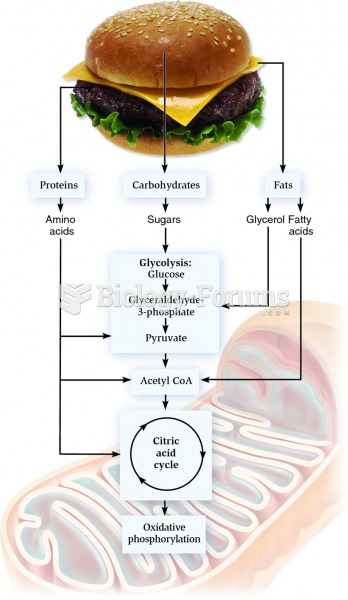
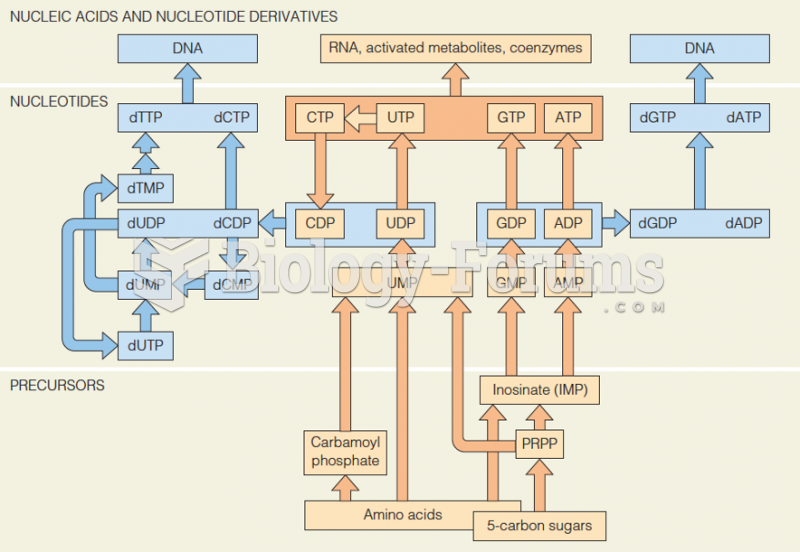
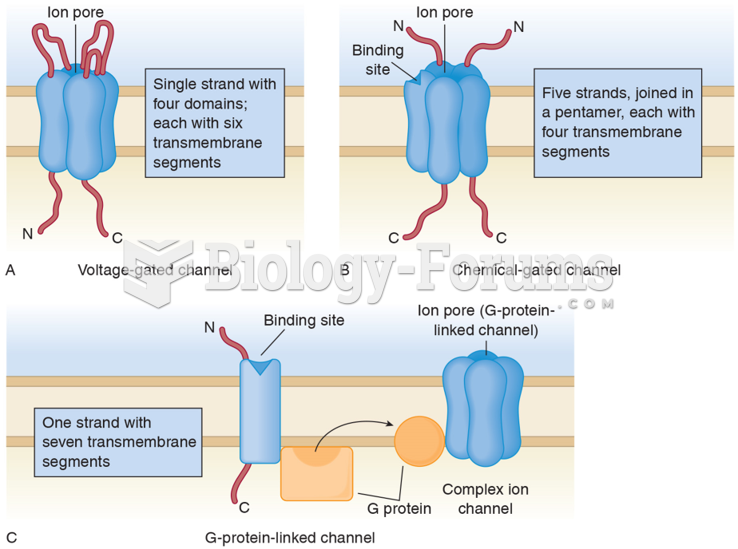
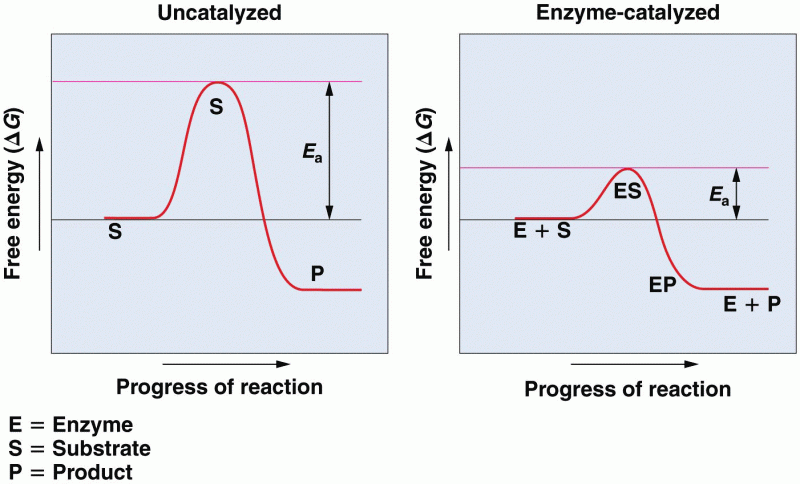
|
|
|
For high blood pressure (hypertension), a new class of drug, called a vasopeptidase blocker (inhibitor), has been developed. It decreases blood pressure by simultaneously dilating the peripheral arteries and increasing the body's loss of salt.
Vampire bats have a natural anticoagulant in their saliva that permits continuous bleeding after they painlessly open a wound with their incisors. This capillary blood does not cause any significant blood loss to their victims.
The first documented use of surgical anesthesia in the United States was in Connecticut in 1844.
Common abbreviations that cause medication errors include U (unit), mg (milligram), QD (every day), SC (subcutaneous), TIW (three times per week), D/C (discharge or discontinue), HS (at bedtime or "hours of sleep"), cc (cubic centimeters), and AU (each ear).
Bisphosphonates were first developed in the nineteenth century. They were first investigated for use in disorders of bone metabolism in the 1960s. They are now used clinically for the treatment of osteoporosis, Paget's disease, bone metastasis, multiple myeloma, and other conditions that feature bone fragility.