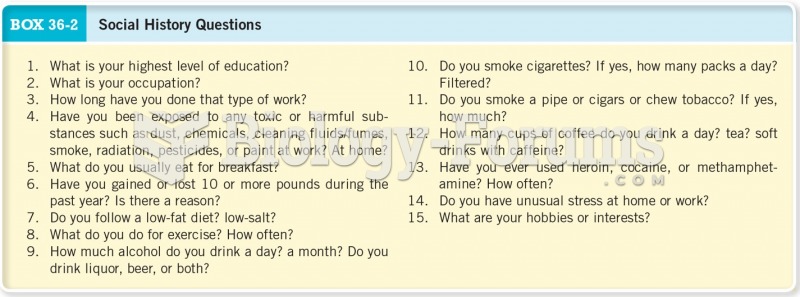
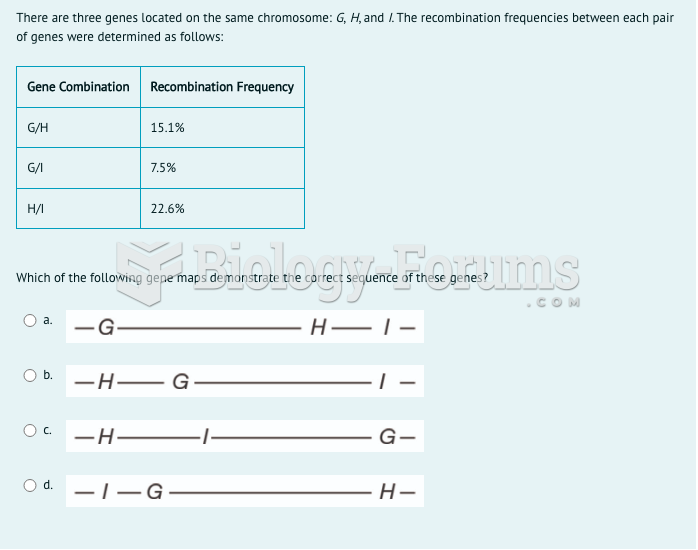
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
If you could remove all of your skin, it would weigh up to 5 pounds.
Did you know?
Computer programs are available that crosscheck a new drug's possible trade name with all other trade names currently available. These programs detect dangerous similarities between names and alert the manufacturer of the drug.
Did you know?
Many of the drugs used by neuroscientists are derived from toxic plants and venomous animals (such as snakes, spiders, snails, and puffer fish).
Did you know?
There are 20 feet of blood vessels in each square inch of human skin.
Did you know?
Only 12 hours after an egg cell is fertilized by a sperm cell, the egg cell starts to divide. As it continues to divide, it moves along the fallopian tube toward the uterus at about 1 inch per day.