Answer to Question 1
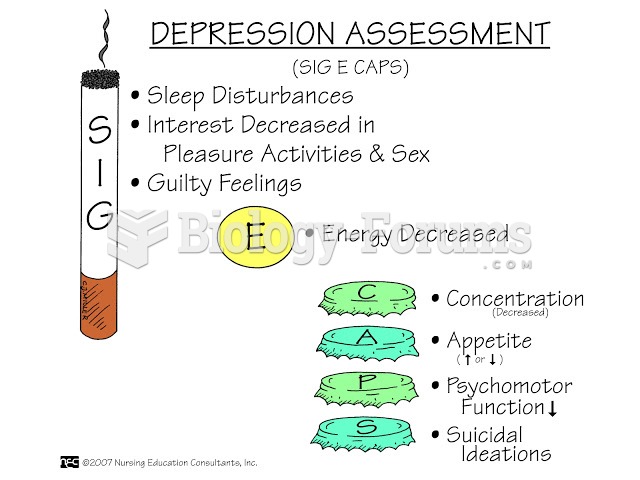
As a symptom, depression refers to feeling sad or miserable. Depressive symptoms often occur without the existence of a serious problem, and they are relatively common at all ages. As a syndrome, depression is more than a sad mood. A syndrome refers to a group of symptoms that occur together more often than by chance. Along with sadness, the child may display a reduced interest or pleasure in activities, cognitive and motivational changes, and somatic and psychomotor changes. As a syndrome, depression represents an extreme on a dimension reflecting the number or severity of co-occurring symptoms that the child displays. As a disorder, depression comes in several forms. We will consider three types. The first, major depressive disorder (MDD), has a minimum duration of 2 weeks and includes low mood, loss of interest or pleasure, other symptoms (e.g., sleep disturbances, difficulty concentrating, feelings of worthlessness), and significant distress or impairment in functioning. The second, persistent depressive disorder (PDD), or dysthymia, is associated with depressed or irritable mood, generally fewer, less severe, but longer-lasting symptoms (a year or more in children) than MDD, and significant impairment in functioning. The third, disruptive mood dysregulation disorder (DMDD), is a recently introduced depressive disorder characterized by: 1 . frequent and severe temper outbursts that are extreme overreactions to the situation or provocation; and 2 . chronic, persistently irritable or angry mood that is present between the severe temper outbursts.
Answer to Question 2
Children express and experience depression differently at different ages (Weiss & Garber, 2003). An infant may show sadness by being passive and unresponsive; a preschooler may appear withdrawn and inhibited; a school-age child may be argumentative and combative or complain of feeling sick; a teenager may express feelings of guilt and hopelessness, sulk, or feel misunderstood. These examples are not various types of depressions, but likely represent different stages in the developmental course of the same process.