|
|
|
The most destructive flu epidemic of all times in recorded history occurred in 1918, with approximately 20 million deaths worldwide.
Of the estimated 2 million heroin users in the United States, 600,000–800,000 are considered hardcore addicts. Heroin addiction is considered to be one of the hardest addictions to recover from.
All patients with hyperparathyroidism will develop osteoporosis. The parathyroid glands maintain blood calcium within the normal range. All patients with this disease will continue to lose calcium from their bones every day, and there is no way to prevent the development of osteoporosis as a result.
The B-complex vitamins and vitamin C are not stored in the body and must be replaced each day.
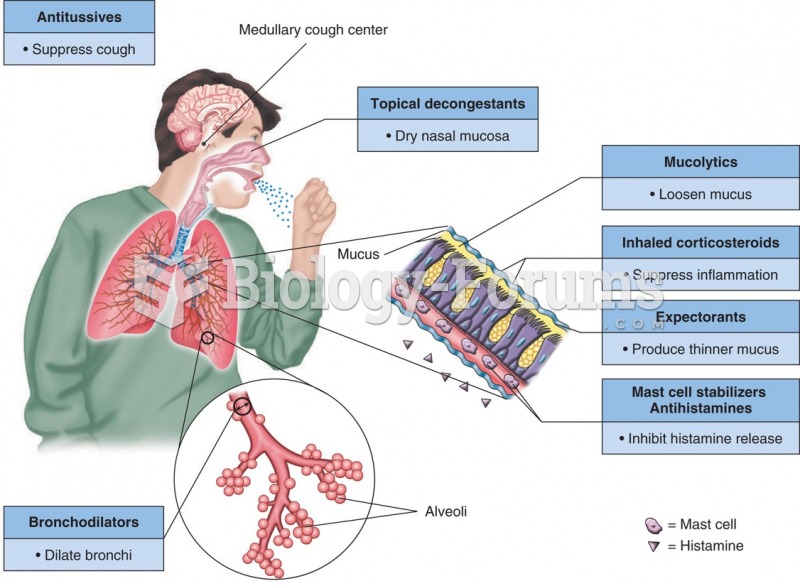
Common abbreviations that cause medication errors include U (unit), mg (milligram), QD (every day), SC (subcutaneous), TIW (three times per week), D/C (discharge or discontinue), HS (at bedtime or "hours of sleep"), cc (cubic centimeters), and AU (each ear).