|
|
|
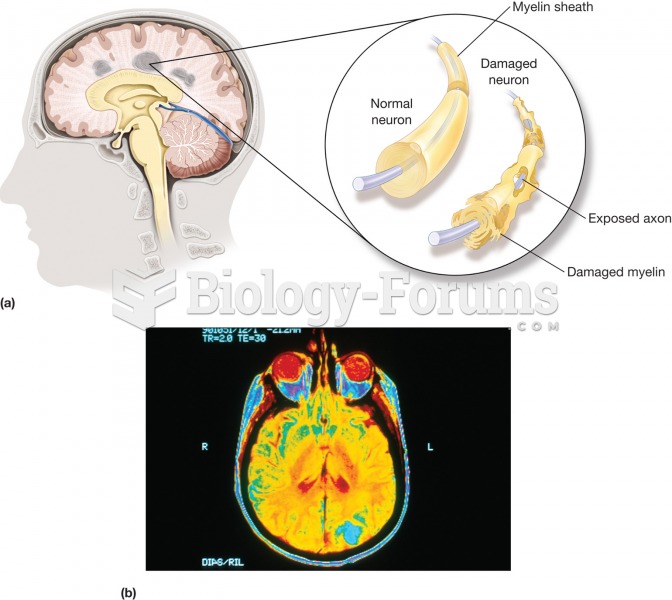
Addicts to opiates often avoid treatment because they are afraid of withdrawal. Though unpleasant, with proper management, withdrawal is rarely fatal and passes relatively quickly.
Side effects from substance abuse include nausea, dehydration, reduced productivitiy, and dependence. Though these effects usually worsen over time, the constant need for the substance often overcomes rational thinking.
In the United States, an estimated 50 million unnecessary antibiotics are prescribed for viral respiratory infections.
Eating carrots will improve your eyesight. Carrots are high in vitamin A (retinol), which is essential for good vision. It can also be found in milk, cheese, egg yolks, and liver.
Eating food that has been cooked with poppy seeds may cause you to fail a drug screening test, because the seeds contain enough opiate alkaloids to register as a positive.