|
|
|
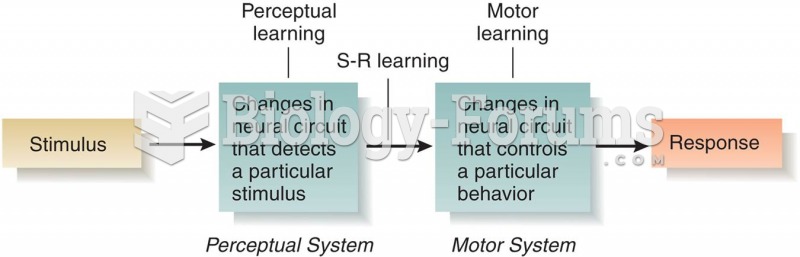
Drug abusers experience the following scenario: The pleasure given by their drug (or drugs) of choice is so strong that it is difficult to eradicate even after years of staying away from the substances involved. Certain triggers may cause a drug abuser to relapse. Research shows that long-term drug abuse results in significant changes in brain function that persist long after an individual stops using drugs. It is most important to realize that the same is true of not just illegal substances but alcohol and tobacco as well.
Each year in the United States, there are approximately six million pregnancies. This means that at any one time, about 4% of women in the United States are pregnant.
In 1885, the Lloyd Manufacturing Company of Albany, New York, promoted and sold "Cocaine Toothache Drops" at 15 cents per bottle! In 1914, the Harrison Narcotic Act brought the sale and distribution of this drug under federal control.
Dogs have been used in studies to detect various cancers in human subjects. They have been trained to sniff breath samples from humans that were collected by having them breathe into special tubes. These people included 55 lung cancer patients, 31 breast cancer patients, and 83 cancer-free patients. The dogs detected 54 of the 55 lung cancer patients as having cancer, detected 28 of the 31 breast cancer patients, and gave only three false-positive results (detecting cancer in people who didn't have it).
After 5 years of being diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, one every three patients will no longer be able to work.