|
|
|
Dogs have been used in studies to detect various cancers in human subjects. They have been trained to sniff breath samples from humans that were collected by having them breathe into special tubes. These people included 55 lung cancer patients, 31 breast cancer patients, and 83 cancer-free patients. The dogs detected 54 of the 55 lung cancer patients as having cancer, detected 28 of the 31 breast cancer patients, and gave only three false-positive results (detecting cancer in people who didn't have it).
The modern decimal position system was the invention of the Hindus (around 800 AD), involving the placing of numerals to indicate their value (units, tens, hundreds, and so on).
Though “Krazy Glue” or “Super Glue” has the ability to seal small wounds, it is not recommended for this purpose since it contains many substances that should not enter the body through the skin, and may be harmful.
Thyroid conditions cause a higher risk of fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome.
Vaccines cause herd immunity. If the majority of people in a community have been vaccinated against a disease, an unvaccinated person is less likely to get the disease since others are less likely to become sick from it and spread the disease.
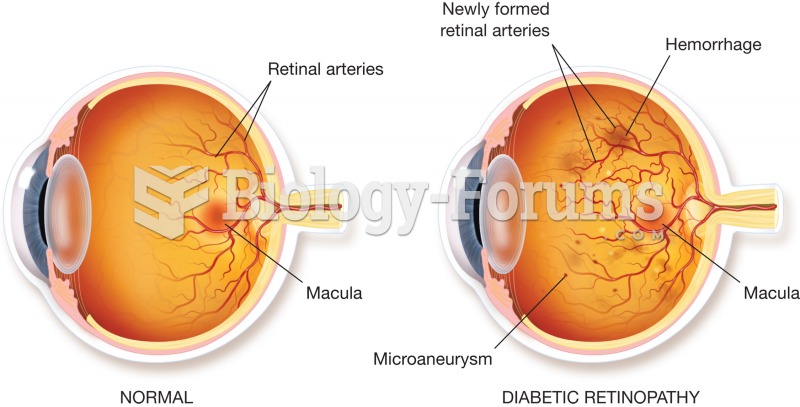 Retinopathy. Illustration of a normal retina (left) and a diseased retina (right). The diseased reti
Retinopathy. Illustration of a normal retina (left) and a diseased retina (right). The diseased reti
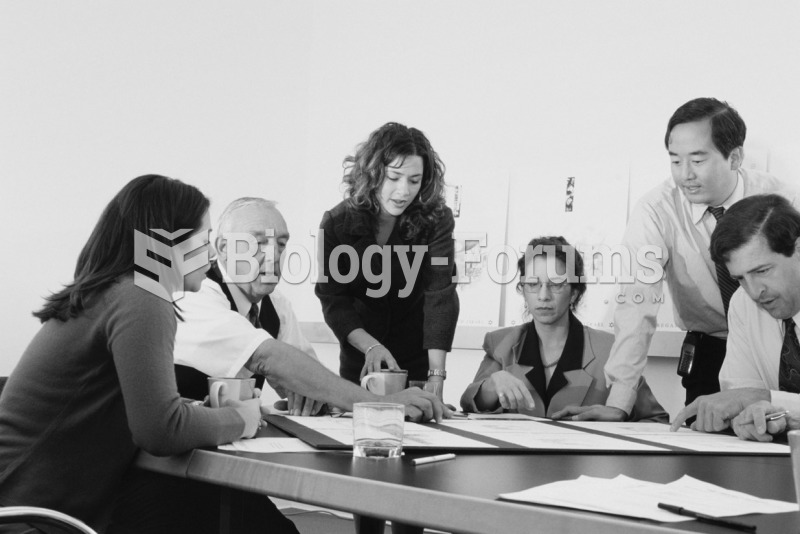 In many work settings, middle-aged people demonstrate generativity by serving as mentors for their ...
In many work settings, middle-aged people demonstrate generativity by serving as mentors for their ...