|
|
|
Each year in the United States, there are approximately six million pregnancies. This means that at any one time, about 4% of women in the United States are pregnant.
All adults should have their cholesterol levels checked once every 5 years. During 2009–2010, 69.4% of Americans age 20 and older reported having their cholesterol checked within the last five years.
Green tea is able to stop the scent of garlic or onion from causing bad breath.
Excessive alcohol use costs the country approximately $235 billion every year.
An identified risk factor for osteoporosis is the intake of excessive amounts of vitamin A. Dietary intake of approximately double the recommended daily amount of vitamin A, by women, has been shown to reduce bone mineral density and increase the chances for hip fractures compared with women who consumed the recommended daily amount (or less) of vitamin A.
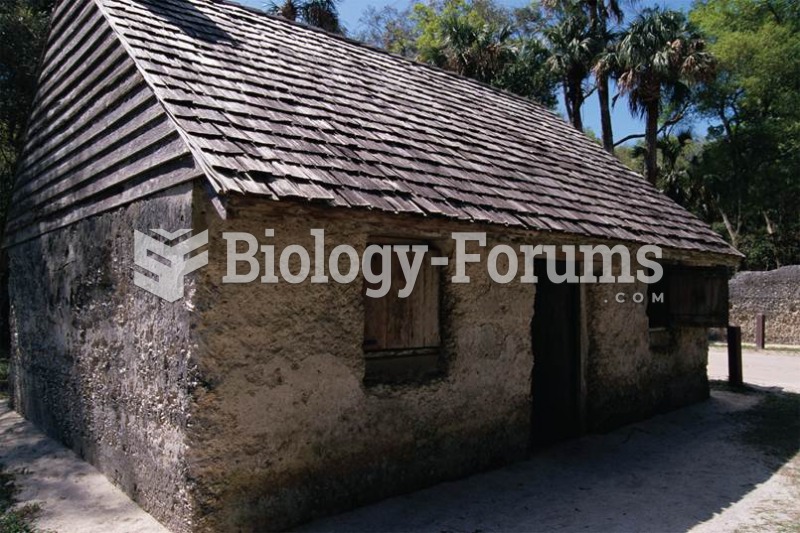 The Kingsley plantation, on Fort George Island in Jacksonville, Florida. Zephaniah Kingsley, the own
The Kingsley plantation, on Fort George Island in Jacksonville, Florida. Zephaniah Kingsley, the own
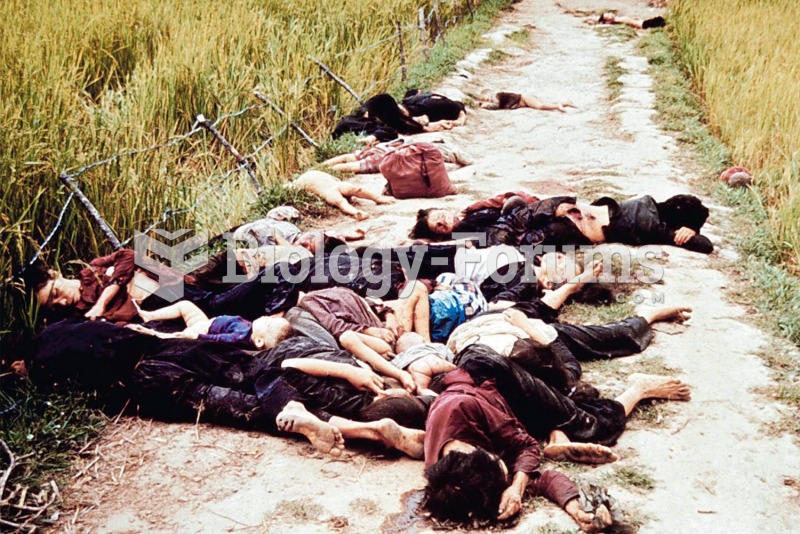 South Vietnamese women and children were among some 300 apparently unarmed civilians killed in a ...
South Vietnamese women and children were among some 300 apparently unarmed civilians killed in a ...