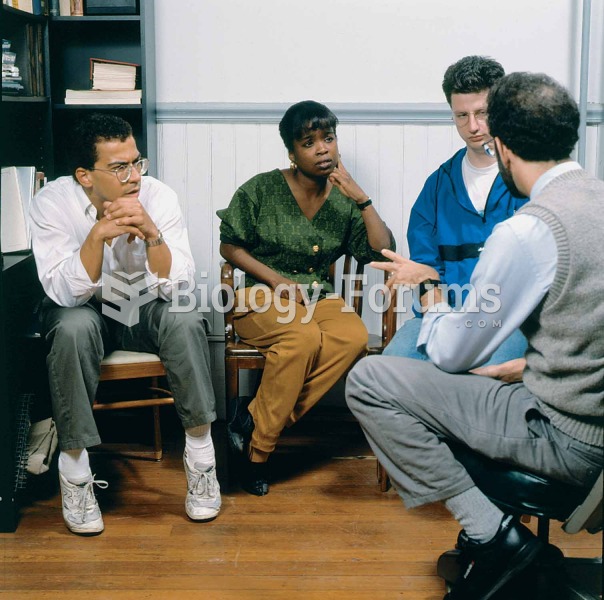
|
|
|
Although not all of the following muscle groups are commonly used, intramuscular injections may be given into the abdominals, biceps, calves, deltoids, gluteals, laterals, pectorals, quadriceps, trapezoids, and triceps.
Limit intake of red meat and dairy products made with whole milk. Choose skim milk, low-fat or fat-free dairy products. Limit fried food. Use healthy oils when cooking.
Your chance of developing a kidney stone is 1 in 10. In recent years, approximately 3.7 million people in the United States were diagnosed with a kidney disease.
Chronic marijuana use can damage the white blood cells and reduce the immune system's ability to respond to disease by as much as 40%. Without a strong immune system, the body is vulnerable to all kinds of degenerative and infectious diseases.
As many as 28% of hospitalized patients requiring mechanical ventilators to help them breathe (for more than 48 hours) will develop ventilator-associated pneumonia. Current therapy involves intravenous antibiotics, but new antibiotics that can be inhaled (and more directly treat the infection) are being developed.