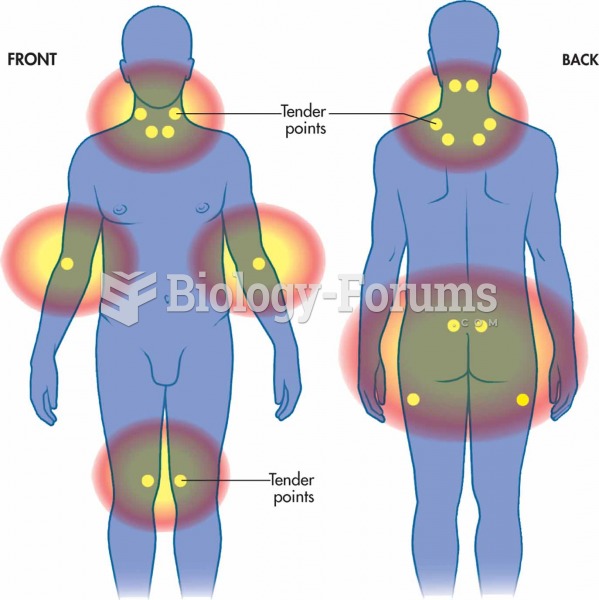
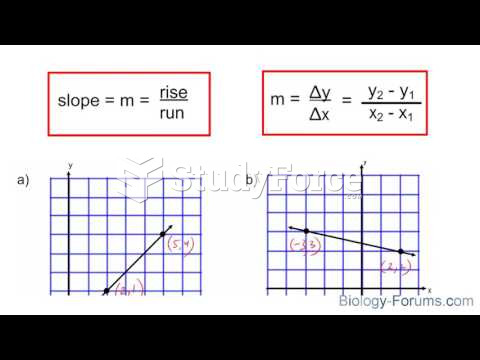
|
|
|
The Romans did not use numerals to indicate fractions but instead used words to indicate parts of a whole.
The average office desk has 400 times more bacteria on it than a toilet.
Limit intake of red meat and dairy products made with whole milk. Choose skim milk, low-fat or fat-free dairy products. Limit fried food. Use healthy oils when cooking.
The tallest man ever known was Robert Wadlow, an American, who reached the height of 8 feet 11 inches. He died at age 26 years from an infection caused by the immense weight of his body (491 pounds) and the stress on his leg bones and muscles.
Eating carrots will improve your eyesight. Carrots are high in vitamin A (retinol), which is essential for good vision. It can also be found in milk, cheese, egg yolks, and liver.