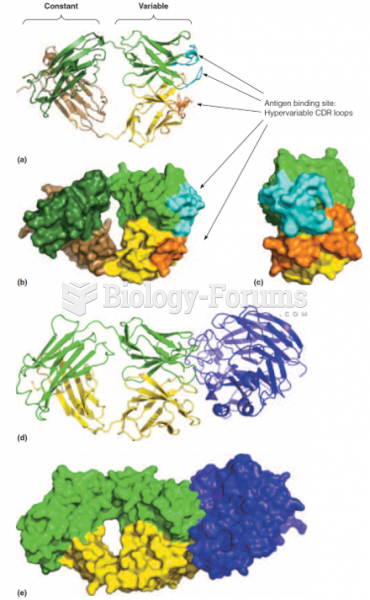
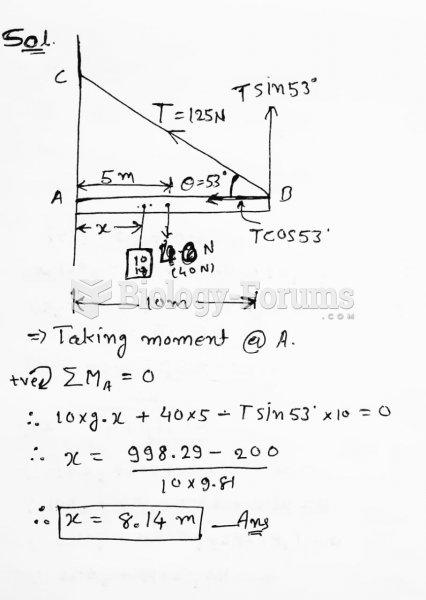
|
|
|
There are 20 feet of blood vessels in each square inch of human skin.
Asthma is the most common chronic childhood disease in the world. Most children who develop asthma have symptoms before they are 5 years old.
Atropine, along with scopolamine and hyoscyamine, is found in the Datura stramonium plant, which gives hallucinogenic effects and is also known as locoweed.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis syndrome are life-threatening reactions that can result in death. Complications include permanent blindness, dry-eye syndrome, lung damage, photophobia, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, permanent loss of nail beds, scarring of mucous membranes, arthritis, and chronic fatigue syndrome. Many patients' pores scar shut, causing them to retain heat.
Long-term mental and physical effects from substance abuse include: paranoia, psychosis, immune deficiencies, and organ damage.
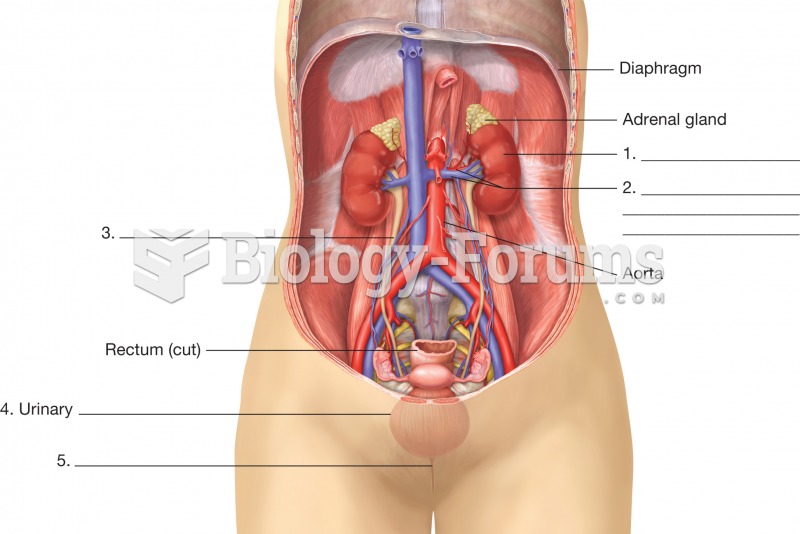 Organs of the urinary system. This illustration is an anterior view of a female with the abdominal w
Organs of the urinary system. This illustration is an anterior view of a female with the abdominal w
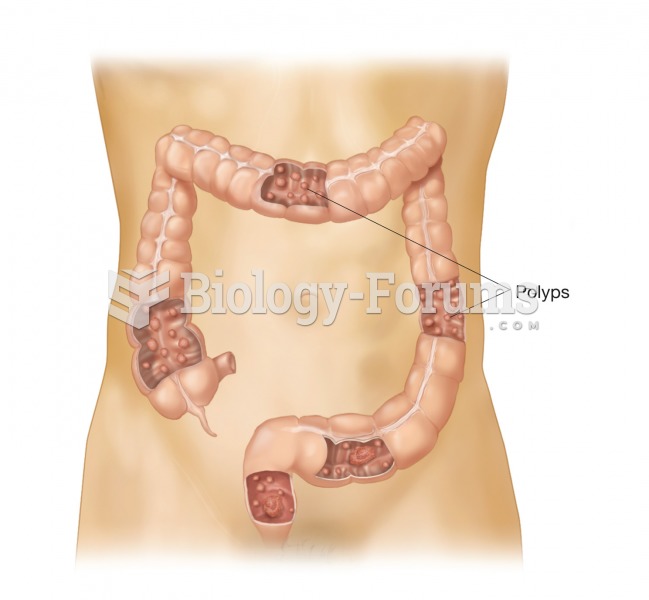 Polyps and polyposis. A polyp is a protruding growth from a mucous membrane lining a hollow organ. I
Polyps and polyposis. A polyp is a protruding growth from a mucous membrane lining a hollow organ. I