Answer to Question 1
A
Answer to Question 2
Chronology: Describes the history of a problem or event from the beginning to the present.
Example: A presentation that describes what has led to the decision to acquire another company
Geography/Space: Presents information organized by geographic region or area or by space or location.
Example: A presentation about the 2015 sales and net profit revenues for each region of an organization
Topic/Function/Conventional Grouping: Presents information organized by specific topics or groups.
Example: A presentation about wireless services offered by a telecommunications company
Comparison/Contrast (Pro/Con): Presents information by comparing one item to others or by showing the pros and cons of an item.
Example: A presentation that shows the pros and cons of allowing employees to telecommute
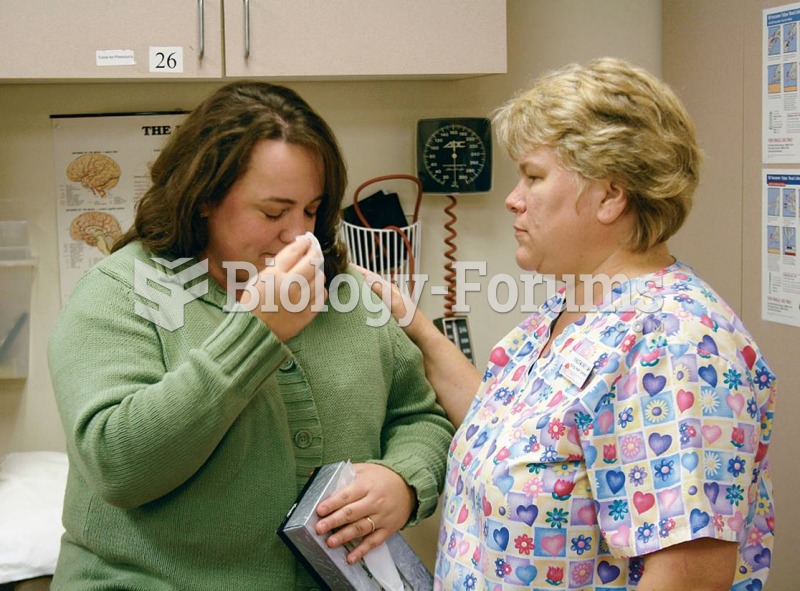
Journalistic Pattern (the five Ws and an H): Answers the questions who, what, when, where, why, and how.
Example: A presentation about an incident of embezzlement within the company
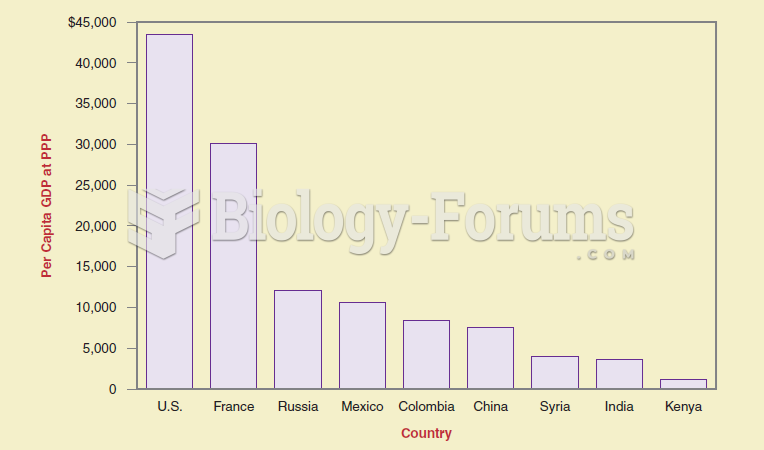
Value/Size: Presents information organized by value or size in increasing or decreasing order.
Example: A presentation about commercial rental costs in the United States, organized from lowest to highest price by city
Importance: Presents information that is organized from the most important reason to the least important, or vice versa.
Example: A presentation about the reasons for decreases in productivity, starting with the most important reason
Problem/Solution: Presents the problem first, followed by a solution.
Example: A presentation about a problem with a network slowdown, followed by a solution for dealing with it
Simple/Complex: Presents information that begins with the simplest concept, leading up to the most complex concept.
Example: A presentation about operating a software package that begins with how to start the software and perform basic operations, leading to how to perform more complex operations
Best Case/Worst Case: Presents a scenario, describing the best possible results and the worst possible results.
Example: A presentation analyzing whether a company should sell its product exclusively online, organized by the best-case result opposed to the worst-case result