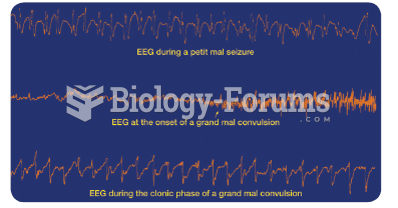
|
|
|
Signs and symptoms that may signify an eye tumor include general blurred vision, bulging eye(s), double vision, a sensation of a foreign body in the eye(s), iris defects, limited ability to move the eyelid(s), limited ability to move the eye(s), pain or discomfort in or around the eyes or eyelids, red or pink eyes, white or cloud spots on the eye(s), colored spots on the eyelid(s), swelling around the eyes, swollen eyelid(s), and general vision loss.
Interferon was scarce and expensive until 1980, when the interferon gene was inserted into bacteria using recombinant DNA technology, allowing for mass cultivation and purification from bacterial cultures.
Of the estimated 2 million heroin users in the United States, 600,000–800,000 are considered hardcore addicts. Heroin addiction is considered to be one of the hardest addictions to recover from.
There are 60,000 miles of blood vessels in every adult human.
According to research, pregnant women tend to eat more if carrying a baby boy. Male fetuses may secrete a chemical that stimulates their mothers to step up her energy intake.
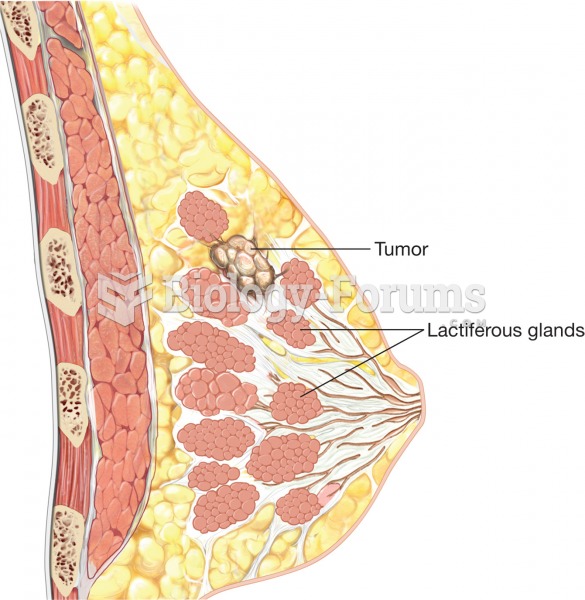 Breast cancer. Notice the tumor growing within a lactiferous gland, which occurs in infiltrating duc
Breast cancer. Notice the tumor growing within a lactiferous gland, which occurs in infiltrating duc
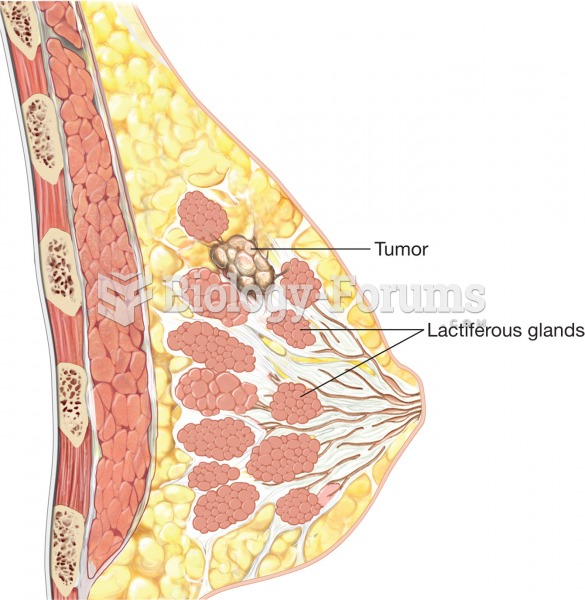 Breast cancer. Notice the tumor growing within a lactiferous gland, which occurs in infiltrating duc
Breast cancer. Notice the tumor growing within a lactiferous gland, which occurs in infiltrating duc
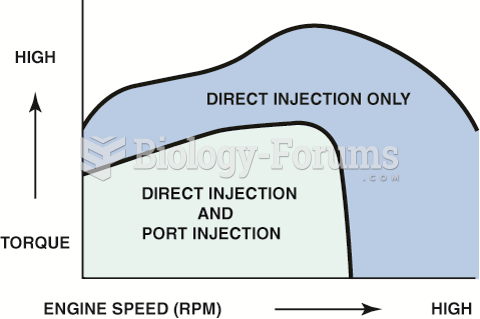 Notice that there are conditions when the port fuel-injector, located in the intake manifold, and ...
Notice that there are conditions when the port fuel-injector, located in the intake manifold, and ...