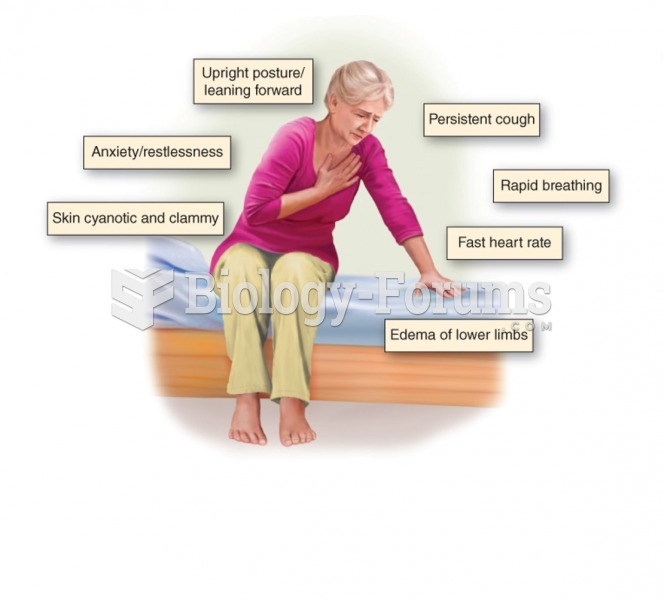
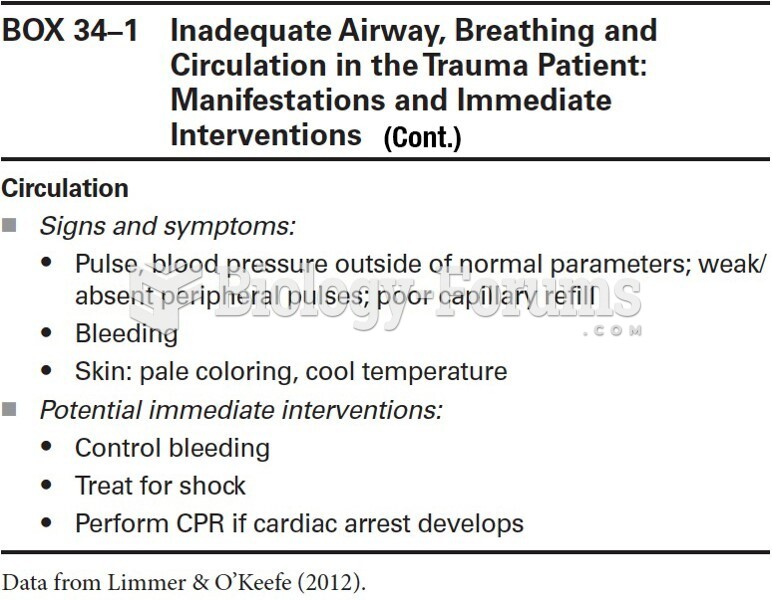
|
|
|
The average person is easily confused by the terms pharmaceutics and pharmacology, thinking they are one and the same. Whereas pharmaceutics is the science of preparing and dispensing drugs (otherwise known as the science of pharmacy), pharmacology is the study of medications.
Medication errors are more common among seriously ill patients than with those with minor conditions.
Medications that are definitely not safe to take when breastfeeding include radioactive drugs, antimetabolites, some cancer (chemotherapy) agents, bromocriptine, ergotamine, methotrexate, and cyclosporine.
Approximately one in four people diagnosed with diabetes will develop foot problems. Of these, about one-third will require lower extremity amputation.
Though newer “smart” infusion pumps are increasingly becoming more sophisticated, they cannot prevent all programming and administration errors. Health care professionals that use smart infusion pumps must still practice the rights of medication administration and have other professionals double-check all high-risk infusions.