Answer to Question 1
C
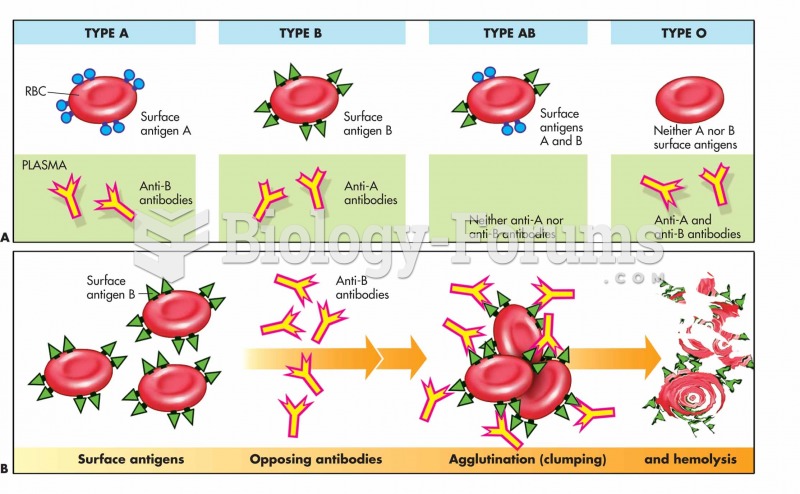
Symptoms of an acute hemolytic reaction usually begin within 15 minutes of transfusion initiation and include severe pain in the kidney area and chest, increased temperature (up to 105F), increased heart rate, and a sensation of heat and pain along the vein receiving blood, as well as chills, low back pain, headache, nausea, chest or back pain, chest tightness, dyspnea, bronchospasm, anxiety, hypotension, vascular collapse, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and possibly death. Symptoms of a delayed hemolytic reaction usually begin 2 to 14 days after the transfusion and include unexplained fever, an unexplained decrease in hemoglobin/hematocrit (Hgb/Hct), increased bilirubin levels, and jaundice. Symptoms of a nonhemolytic febrile reaction begin between 30 minutes after initiation and 6 hours after completion of transfusion and include fever greater than 1 C above baseline, flushing, chills, headache, and muscle pain; they occur most frequently in immunosuppressed patients. Symptoms of an acute severe allergic reaction usually begin within 5 to 15 minutes of initiation of transfusion and include coughing, nausea, vomiting, respiratory distress, wheezing, hypotension, loss of consciousness, and possible cardiac arrest.
Answer to Question 2
A
Observe the patient for wheezing, chest pain, and possible cardiac arrest. All of these are indications of an anaphylactic reaction. Be alert to patient complaints of headache or muscle pain in the presence of a fever. Both may be indicative of a febrile nonhemolytic reaction. Observe patients receiving massive transfusions for mild hypothermia, cardiac dysrhythmias, hypotension, and hypocalcemia. Cold blood products can affect the cardiac conduction system, resulting in ventricular dysrhythmias. Other cardiac dysrhythmias, hypotension, and tingling may indicate hypocalcemia, which occurs when citrate (used as a preservative for some blood products) combines with the patient's calcium. Crackles in the bases of lungs and rising central venous pressure (CVP) are indications of circulatory overload.