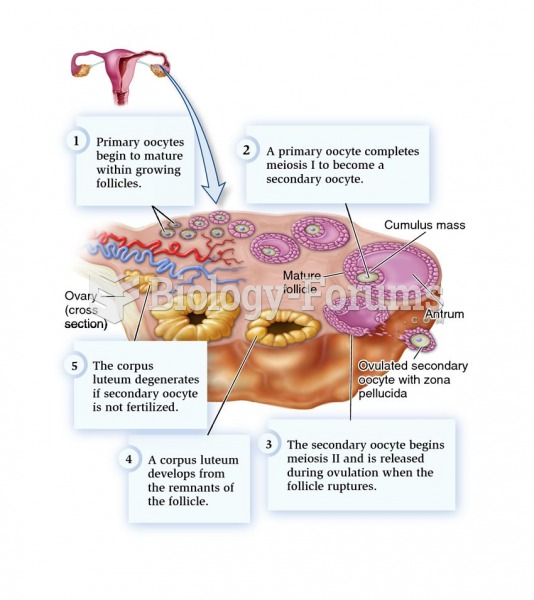
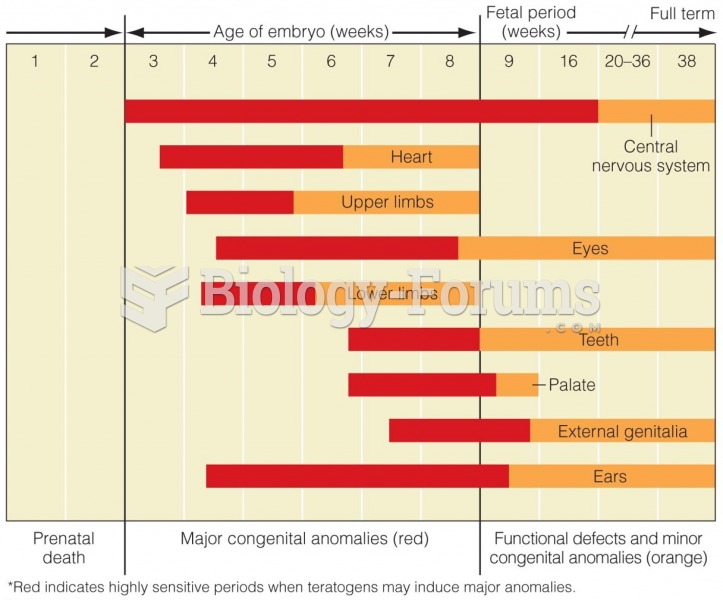
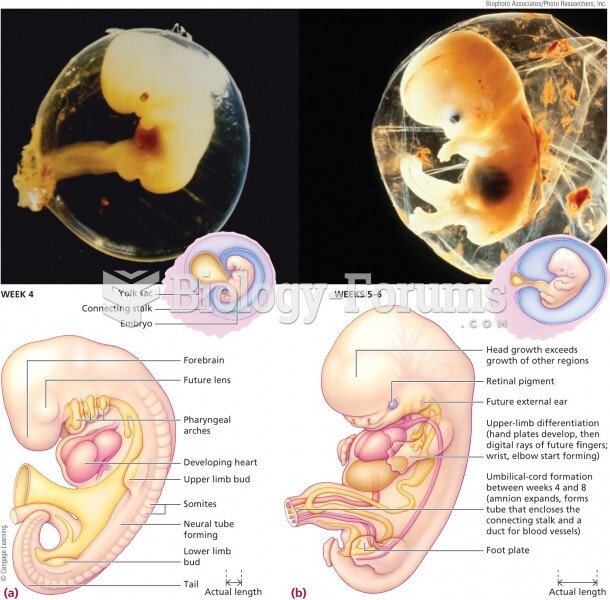
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Eat fiber! A diet high in fiber can help lower cholesterol levels by as much as 10%.
Did you know?
Malaria was not eliminated in the United States until 1951. The term eliminated means that no new cases arise in a country for 3 years.
Did you know?
The lipid bilayer is made of phospholipids. They are arranged in a double layer because one of their ends is attracted to water while the other is repelled by water.
Did you know?
When intravenous medications are involved in adverse drug events, their harmful effects may occur more rapidly, and be more severe than errors with oral medications. This is due to the direct administration into the bloodstream.
Did you know?
When blood is exposed to air, it clots. Heparin allows the blood to come in direct contact with air without clotting.