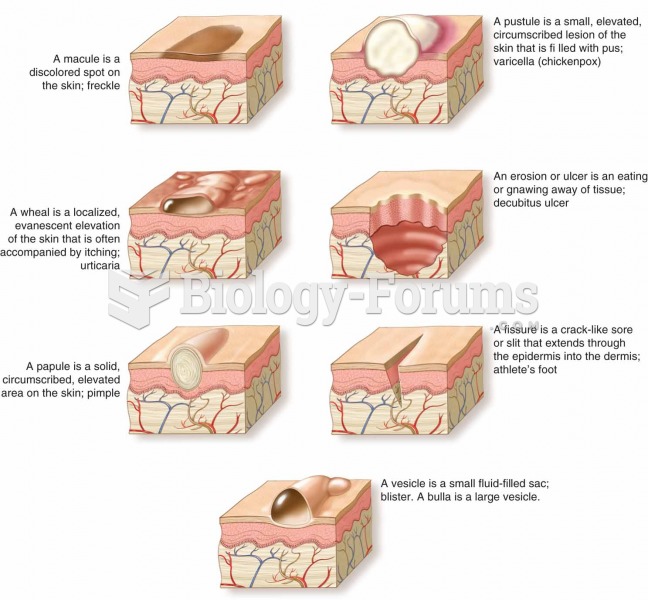
|
|
|
More than 30% of American adults, and about 12% of children utilize health care approaches that were developed outside of conventional medicine.
Elderly adults are at greatest risk of stroke and myocardial infarction and have the most to gain from prophylaxis. Patients ages 60 to 80 years with blood pressures above 160/90 mm Hg should benefit from antihypertensive treatment.
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
Chronic necrotizing aspergillosis has a slowly progressive process that, unlike invasive aspergillosis, does not spread to other organ systems or the blood vessels. It most often affects middle-aged and elderly individuals, spreading to surrounding tissue in the lungs. The disease often does not respond to conventionally successful treatments, and requires individualized therapies in order to keep it from becoming life-threatening.
Many of the drugs used by neuroscientists are derived from toxic plants and venomous animals (such as snakes, spiders, snails, and puffer fish).