|
|
|
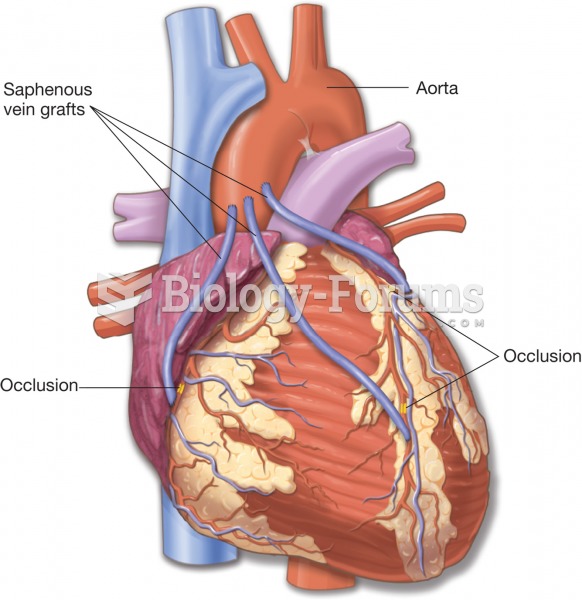
People with high total cholesterol have about two times the risk for heart disease as people with ideal levels.
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.
Asthma occurs in one in 11 children and in one in 12 adults. African Americans and Latinos have a higher risk for developing asthma than other groups.
To prove that stomach ulcers were caused by bacteria and not by stress, a researcher consumed an entire laboratory beaker full of bacterial culture. After this, he did indeed develop stomach ulcers, and won the Nobel Prize for his discovery.
Most fungi that pathogenically affect humans live in soil. If a person is not healthy, has an open wound, or is immunocompromised, a fungal infection can be very aggressive.