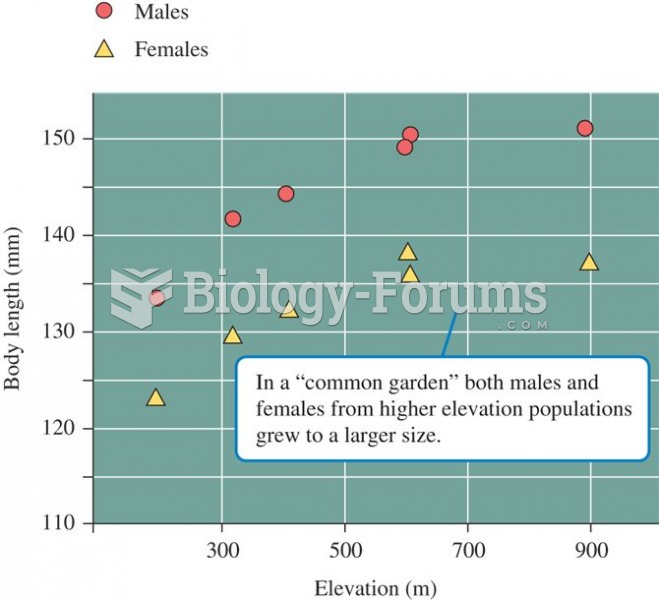
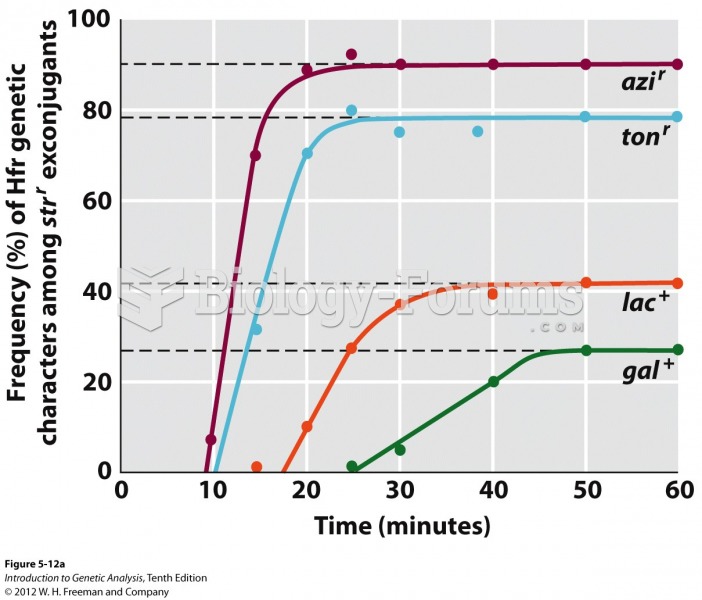
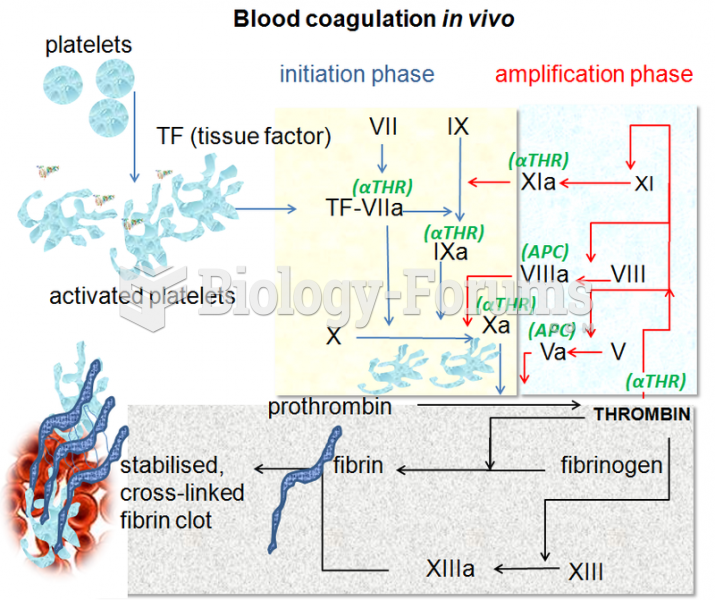
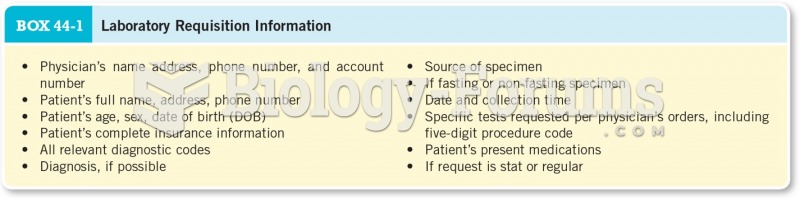
|
|
|
An identified risk factor for osteoporosis is the intake of excessive amounts of vitamin A. Dietary intake of approximately double the recommended daily amount of vitamin A, by women, has been shown to reduce bone mineral density and increase the chances for hip fractures compared with women who consumed the recommended daily amount (or less) of vitamin A.
In 2006, a generic antinausea drug named ondansetron was approved. It is used to stop nausea and vomiting associated with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Vaccines prevent between 2.5 and 4 million deaths every year.
The first oncogene was discovered in 1970 and was termed SRC (pronounced "SARK").
A seasonal flu vaccine is the best way to reduce the chances you will get seasonal influenza and spread it to others.