|
|
|
Coca-Cola originally used coca leaves and caffeine from the African kola nut. It was advertised as a therapeutic agent and "pickerupper." Eventually, its formulation was changed, and the coca leaves were removed because of the effects of regulation on cocaine-related products.
Aspirin may benefit 11 different cancers, including those of the colon, pancreas, lungs, prostate, breasts, and leukemia.
There are major differences in the metabolism of morphine and the illegal drug heroin. Morphine mostly produces its CNS effects through m-receptors, and at k- and d-receptors. Heroin has a slight affinity for opiate receptors. Most of its actions are due to metabolism to active metabolites (6-acetylmorphine, morphine, and morphine-6-glucuronide).
The term pharmacology is derived from the Greek words pharmakon("claim, medicine, poison, or remedy") and logos ("study").
Between 1999 and 2012, American adults with high total cholesterol decreased from 18.3% to 12.9%
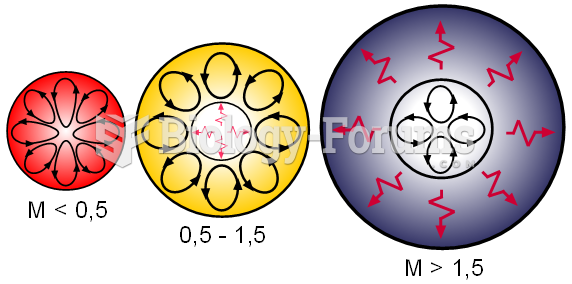 Internal structures of main sequence stars, convection zones with arrowed cycles and radiative zones
Internal structures of main sequence stars, convection zones with arrowed cycles and radiative zones
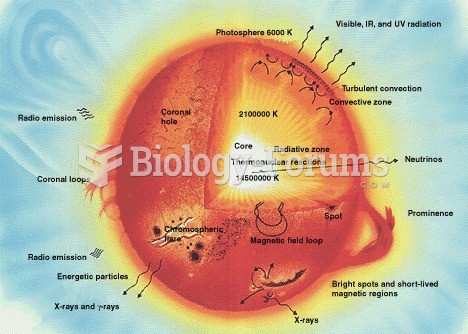 Internal structures of main sequence stars, convection zones with arrowed cycles and radiative zones
Internal structures of main sequence stars, convection zones with arrowed cycles and radiative zones