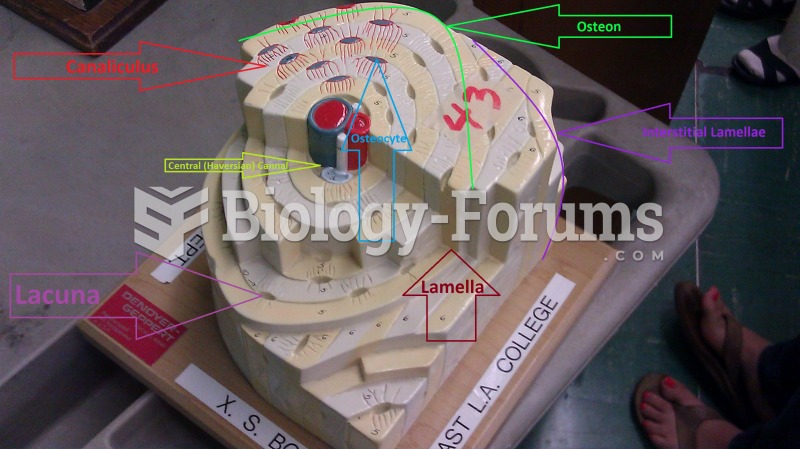
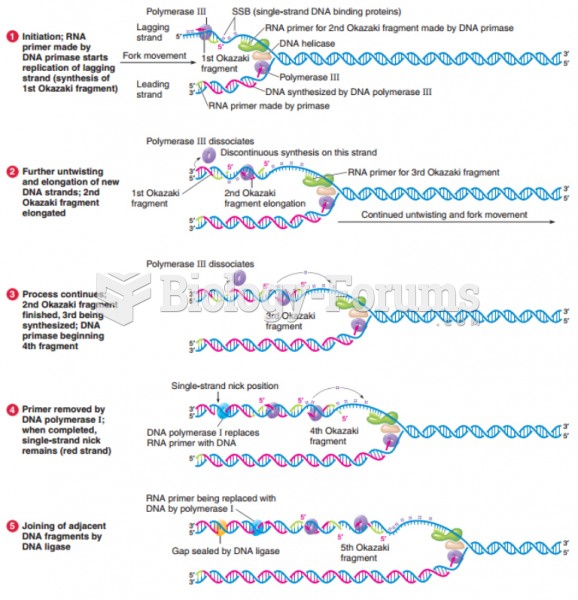
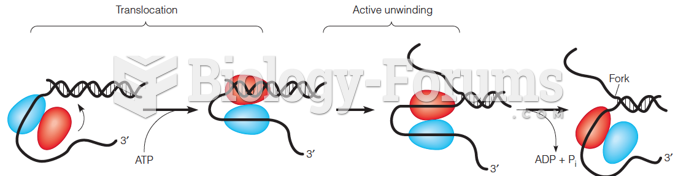
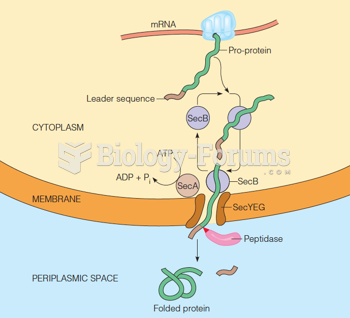
Answer to Question 1
Stage 1: Being Exposed to Information. Exposure simply means that consumers come in contact with the marketer's message. In practical terms, exposing consumers to a brand's message is a function of two key managerial decisions: (1) establishing a sufficient marcom budget, and (2) selecting appropriate media and vehicles in which to present a brand message. Gaining exposure is a necessary but insufficient condition for communication success.
Stage 2: Paying Attention. Attention means to focus cognitive resources on and think about a message to which one has been exposed. Since consumers' information-processing capacity is limited, they will selectively allocate mental energy to only messages that are relevant and of interest to current goals.
Stage 3: Comprehension of What is Attended. The term comprehension often is used interchangeably with perception; both terms refer to interpretation. The perceptual process of interpreting stimuli is called perceptual encoding, and two main stages are involved. Feature analysis is the initial stage whereby a receiver examines the basic features of a stimulus and makes a preliminary classification. The second stage, active synthesis, goes beyond merely examining physical features and considers the context or situation in which information is received.
Stage 4: Agreement with What is Comprehended. It is crucial from a marcom perspective that consumers not only comprehend a message but that they also agree with the message. Agreement depends on whether the message is credible and whether it contains information and appeals that are compatible with the values that are important with the consumer.
Stages 5 and 6: Retention and Search/Retrieval of Stored Information. Both stages involve memory factors. From a marcom perspective, memory involves the related issues of what consumers remember (recognize and recall) about marketing stimuli and how they access and retrieve information when in the process of choosing among product alternatives.
Stages 7 and 8: Deciding From Alternatives and Acting on the Basis of the Decision. These two stages are listed at the beginning of the section on the CPM perspective but are not discussed further in the chapter.
Answer to Question 2
The functions include specifying the value proposition, the target market segment, the value chain and the firm's position in it, the cost structure and profit potential, and its basic competitive strategy.
The conceptual importance of the business model is to help us understand the key elements of an existing or prospective business. The practical importance is that a business plan is an essential part of obtaining start-up capital for a new business. A business model can refer to both online and offline businesses.