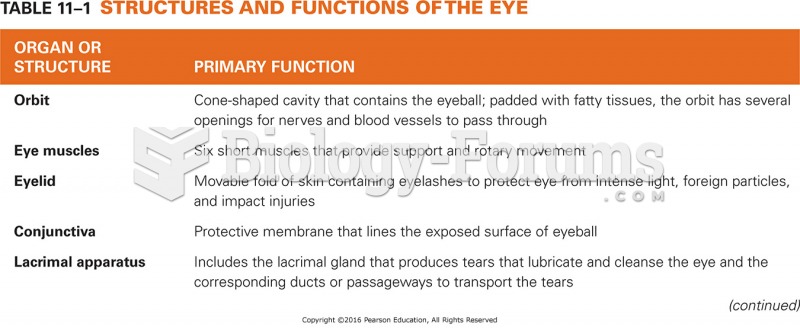
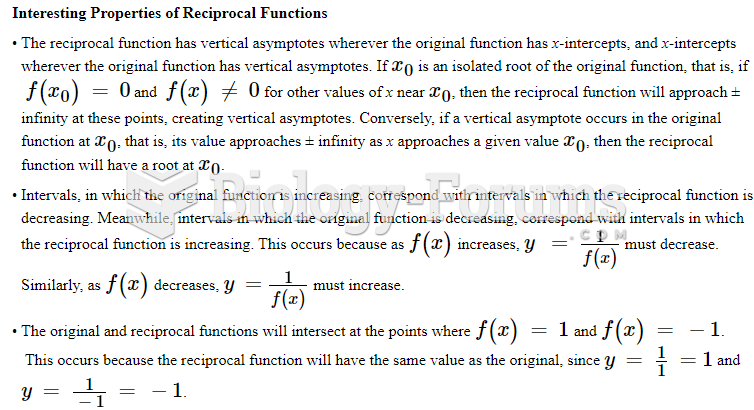
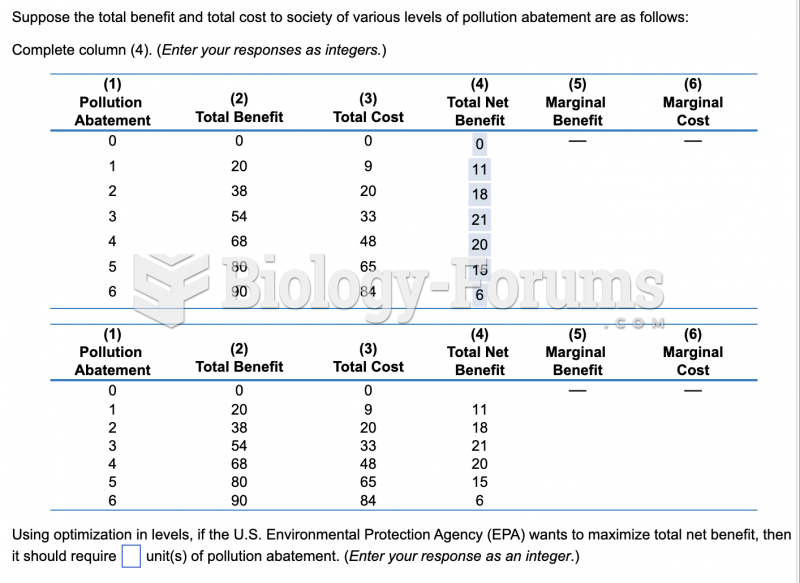
|
|
|
Many of the drugs used by neuroscientists are derived from toxic plants and venomous animals (such as snakes, spiders, snails, and puffer fish).
Human neurons are so small that they require a microscope in order to be seen. However, some neurons can be up to 3 feet long, such as those that extend from the spinal cord to the toes.
A recent study has found that following a diet rich in berries may slow down the aging process of the brain. This diet apparently helps to keep dopamine levels much higher than are seen in normal individuals who do not eat berries as a regular part of their diet as they enter their later years.
In ancient Rome, many of the richer people in the population had lead-induced gout. The reason for this is unclear. Lead poisoning has also been linked to madness.
About 80% of major fungal systemic infections are due to Candida albicans. Another form, Candida peritonitis, occurs most often in postoperative patients. A rare disease, Candida meningitis, may follow leukemia, kidney transplant, other immunosuppressed factors, or when suffering from Candida septicemia.