|
|
|
Critical care patients are twice as likely to receive the wrong medication. Of these errors, 20% are life-threatening, and 42% require additional life-sustaining treatments.
Approximately one in four people diagnosed with diabetes will develop foot problems. Of these, about one-third will require lower extremity amputation.
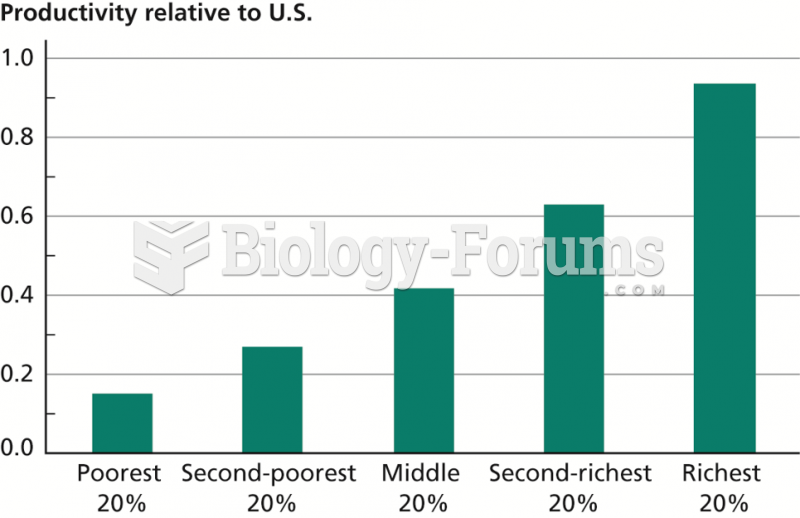
The people with the highest levels of LDL are Mexican American males and non-Hispanic black females.
Tobacco depletes the body of vitamins A, C, and E, which can result in any of the following: dry hair, dry skin, dry eyes, poor growth, night blindness, abscesses, insomnia, fatigue, reproductive system problems, sinusitis, pneumonia, frequent respiratory problems, skin disorders, weight loss, rickets, osteomalacia, nervousness, muscle spasms, leg cramps, extremity numbness, bone malformations, decayed teeth, difficulty in walking, irritability, restlessness, profuse sweating, increased uric acid (gout), joint damage, damaged red blood cells, destruction of nerves, infertility, miscarriage, and many types of cancer.
Although the Roman numeral for the number 4 has always been taught to have been "IV," according to historians, the ancient Romans probably used "IIII" most of the time. This is partially backed up by the fact that early grandfather clocks displayed IIII for the number 4 instead of IV. Early clockmakers apparently thought that the IIII balanced out the VIII (used for the number 8) on the clock face and that it just looked better.