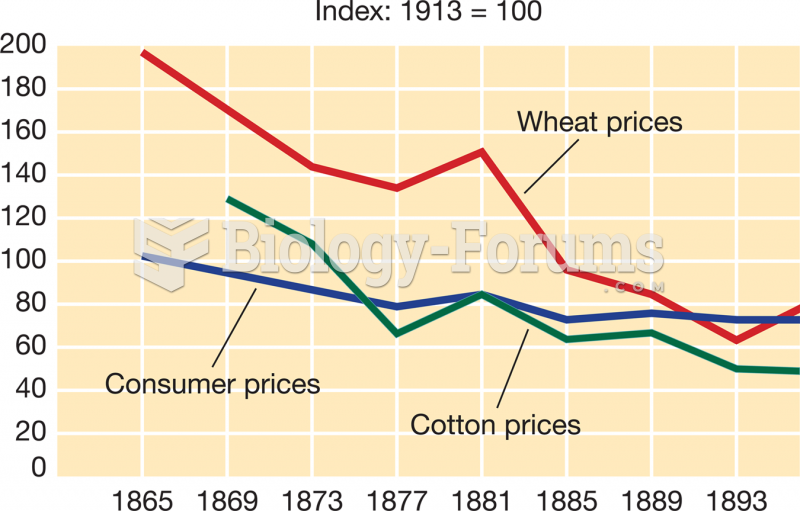
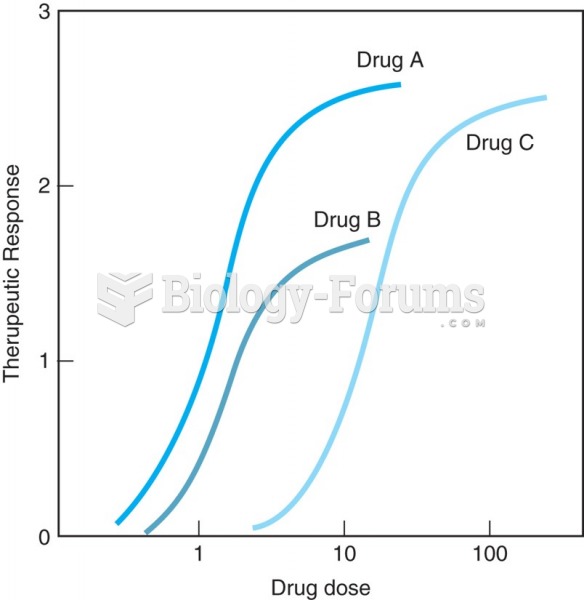
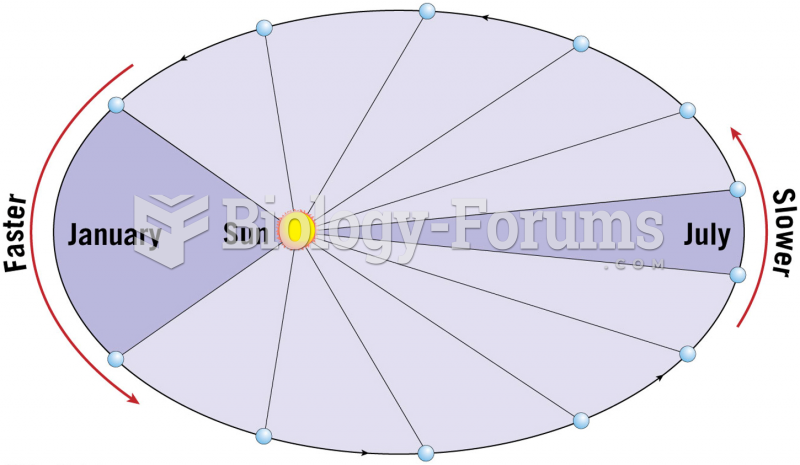
|
|
|
Dogs have been used in studies to detect various cancers in human subjects. They have been trained to sniff breath samples from humans that were collected by having them breathe into special tubes. These people included 55 lung cancer patients, 31 breast cancer patients, and 83 cancer-free patients. The dogs detected 54 of the 55 lung cancer patients as having cancer, detected 28 of the 31 breast cancer patients, and gave only three false-positive results (detecting cancer in people who didn't have it).
In 1835 it was discovered that a disease of silkworms known as muscardine could be transferred from one silkworm to another, and was caused by a fungus.
There are major differences in the metabolism of morphine and the illegal drug heroin. Morphine mostly produces its CNS effects through m-receptors, and at k- and d-receptors. Heroin has a slight affinity for opiate receptors. Most of its actions are due to metabolism to active metabolites (6-acetylmorphine, morphine, and morphine-6-glucuronide).
The training of an anesthesiologist typically requires four years of college, 4 years of medical school, 1 year of internship, and 3 years of residency.
The effects of organophosphate poisoning are referred to by using the abbreviations “SLUD” or “SLUDGE,” It stands for: salivation, lacrimation, urination, defecation, GI upset, and emesis.