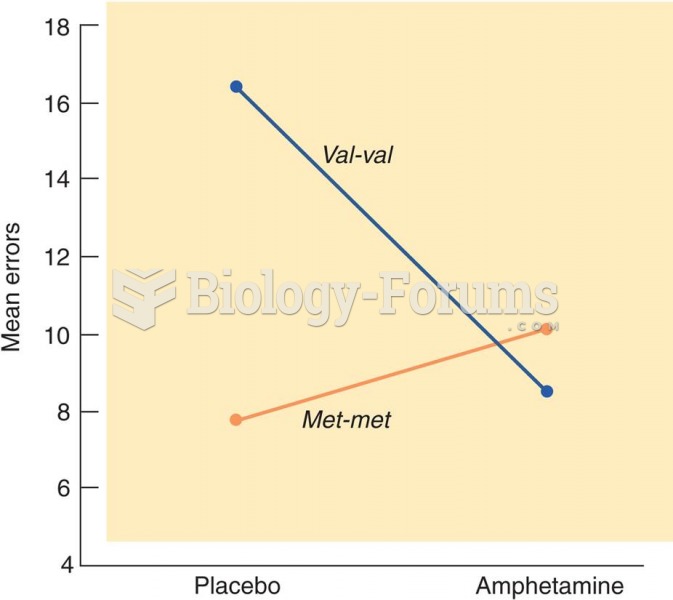
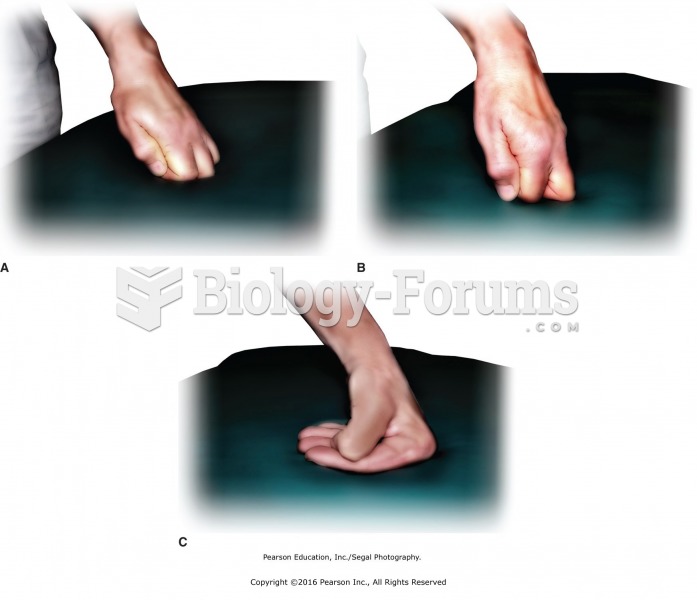
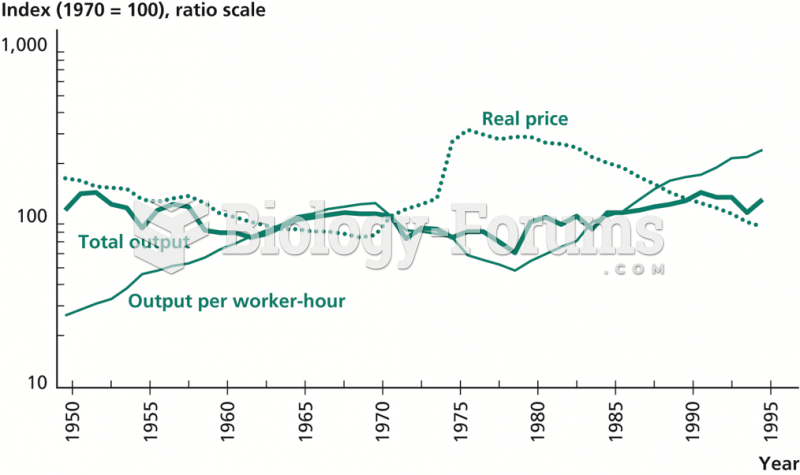
|
|
|
Interferon was scarce and expensive until 1980, when the interferon gene was inserted into bacteria using recombinant DNA technology, allowing for mass cultivation and purification from bacterial cultures.
About 600,000 particles of skin are shed every hour by each human. If you live to age 70 years, you have shed 105 pounds of dead skin.
Parkinson's disease is both chronic and progressive. This means that it persists over a long period of time and that its symptoms grow worse over time.
Nearly all drugs pass into human breast milk. How often a drug is taken influences the amount of drug that will pass into the milk. Medications taken 30 to 60 minutes before breastfeeding are likely to be at peak blood levels when the baby is nursing.
Children with strabismus (crossed eyes) can be treated. They are not able to outgrow this condition on their own, but with help, it can be more easily corrected at a younger age. It is important for infants to have eye examinations as early as possible in their development and then another at age 2 years.
 At breakfast, a middle-class husband sits absorbed in the newspaper and the public affairs of the da
At breakfast, a middle-class husband sits absorbed in the newspaper and the public affairs of the da
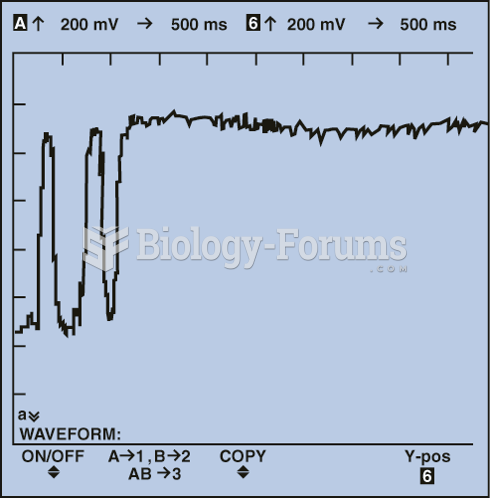 Adding propane to the air inlet of an engine operating in closed loop with a working oxygen sensor ...
Adding propane to the air inlet of an engine operating in closed loop with a working oxygen sensor ...