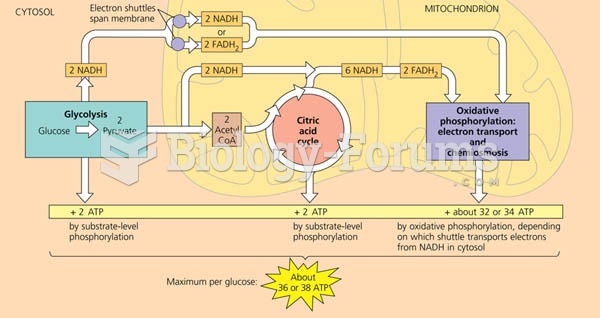
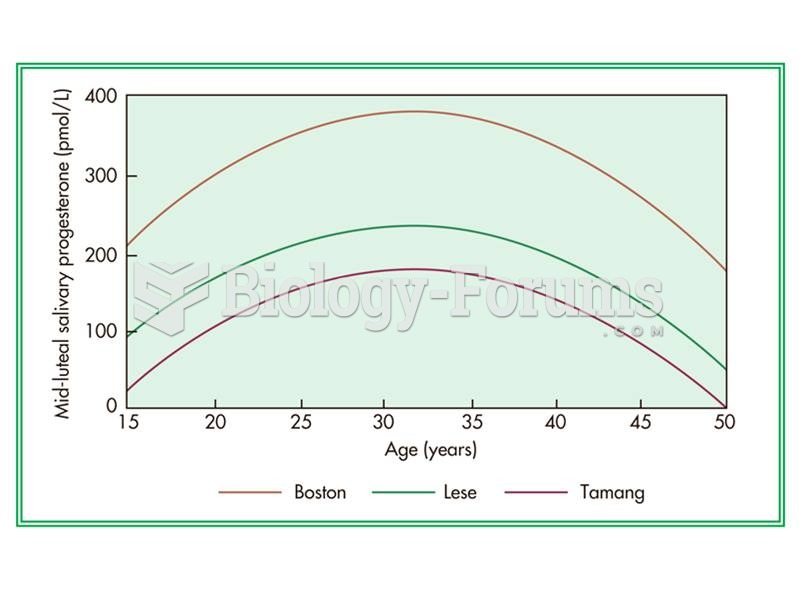
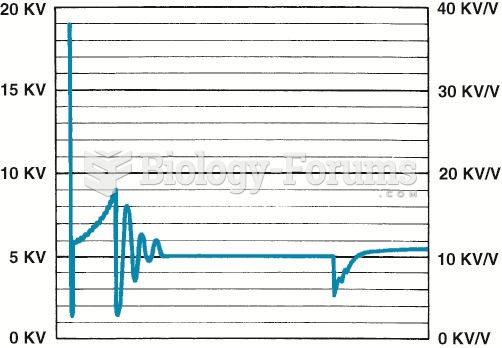
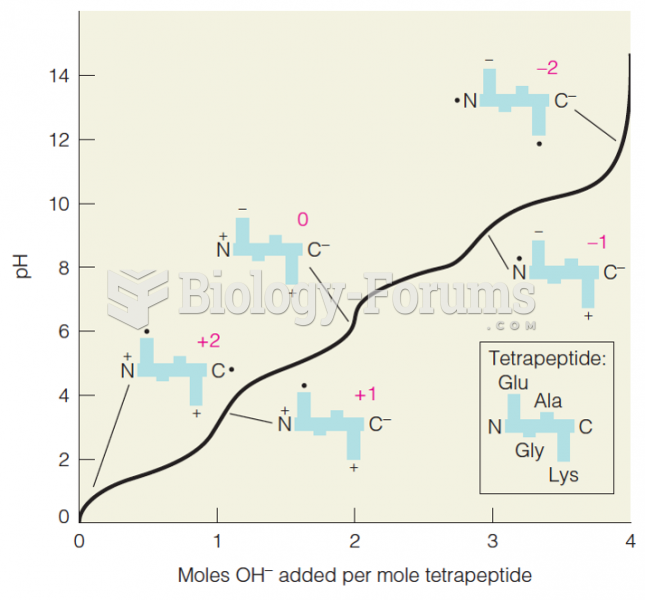
|
|
|
In ancient Rome, many of the richer people in the population had lead-induced gout. The reason for this is unclear. Lead poisoning has also been linked to madness.
Illness; diuretics; laxative abuse; hot weather; exercise; sweating; caffeine; alcoholic beverages; starvation diets; inadequate carbohydrate consumption; and diets high in protein, salt, or fiber can cause people to become dehydrated.
Common abbreviations that cause medication errors include U (unit), mg (milligram), QD (every day), SC (subcutaneous), TIW (three times per week), D/C (discharge or discontinue), HS (at bedtime or "hours of sleep"), cc (cubic centimeters), and AU (each ear).
Many people have small pouches in their colons that bulge outward through weak spots. Each pouch is called a diverticulum. About 10% of Americans older than age 40 years have diverticulosis, which, when the pouches become infected or inflamed, is called diverticulitis. The main cause of diverticular disease is a low-fiber diet.
More than 34,000 trademarked medication names and more than 10,000 generic medication names are in use in the United States.