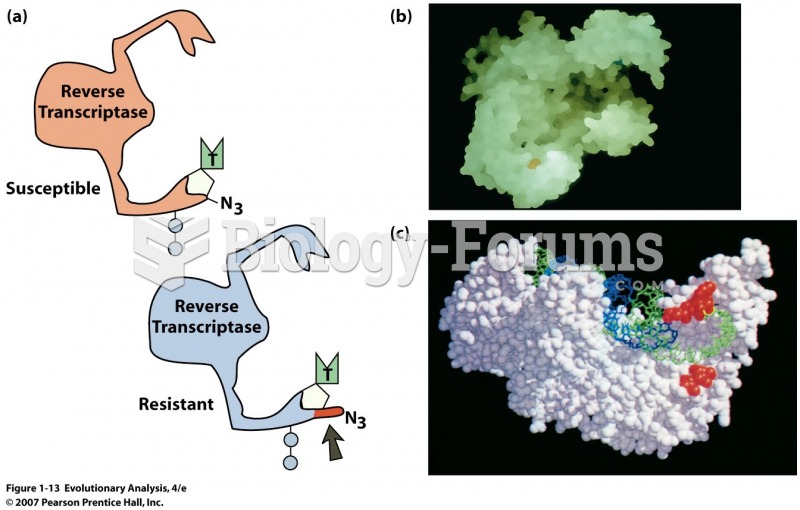
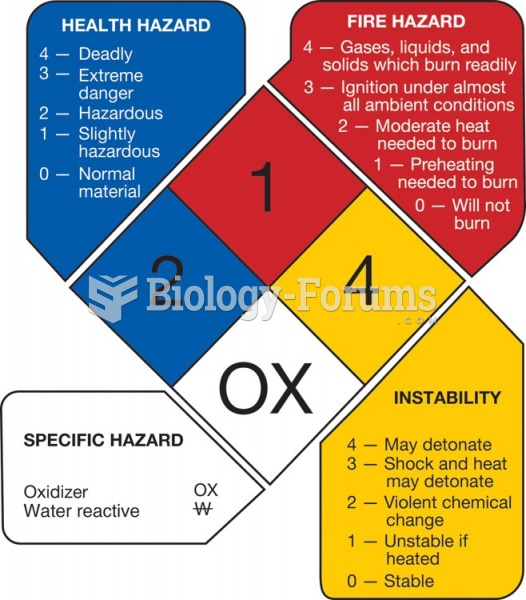
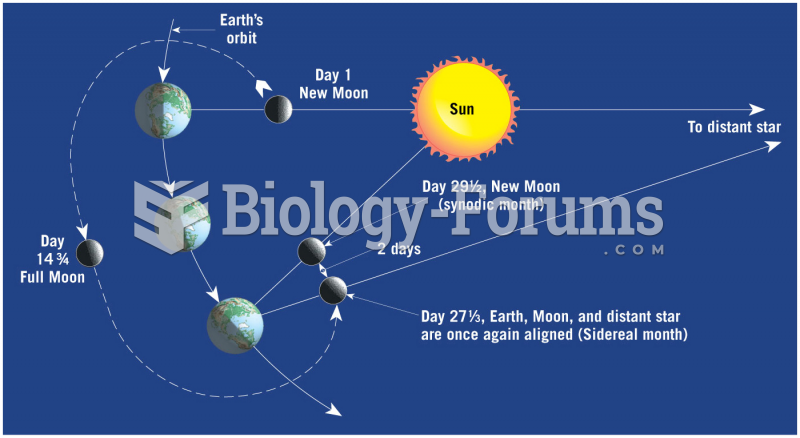
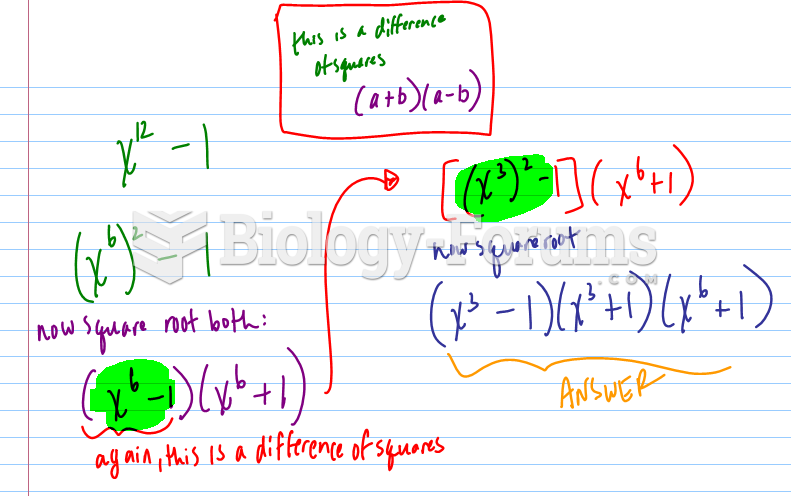
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
During pregnancy, a woman is more likely to experience bleeding gums and nosebleeds caused by hormonal changes that increase blood flow to the mouth and nose.
Did you know?
Warfarin was developed as a consequence of the study of a strange bleeding disorder that suddenly occurred in cattle on the northern prairies of the United States in the early 1900s.
Did you know?
In 1844, Charles Goodyear obtained the first patent for a rubber condom.
Did you know?
Medications that are definitely not safe to take when breastfeeding include radioactive drugs, antimetabolites, some cancer (chemotherapy) agents, bromocriptine, ergotamine, methotrexate, and cyclosporine.
Did you know?
The Romans did not use numerals to indicate fractions but instead used words to indicate parts of a whole.
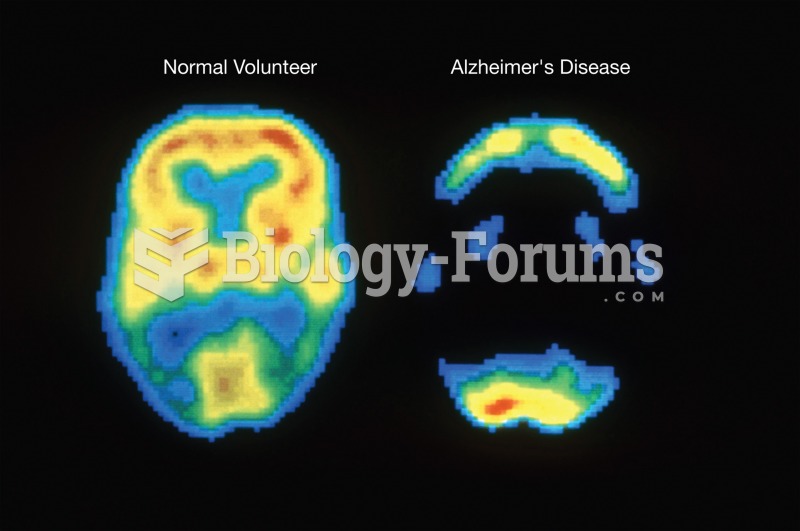 Positron emission tomography (PET) image showing the difference in the metabolic activity of the bra
Positron emission tomography (PET) image showing the difference in the metabolic activity of the bra
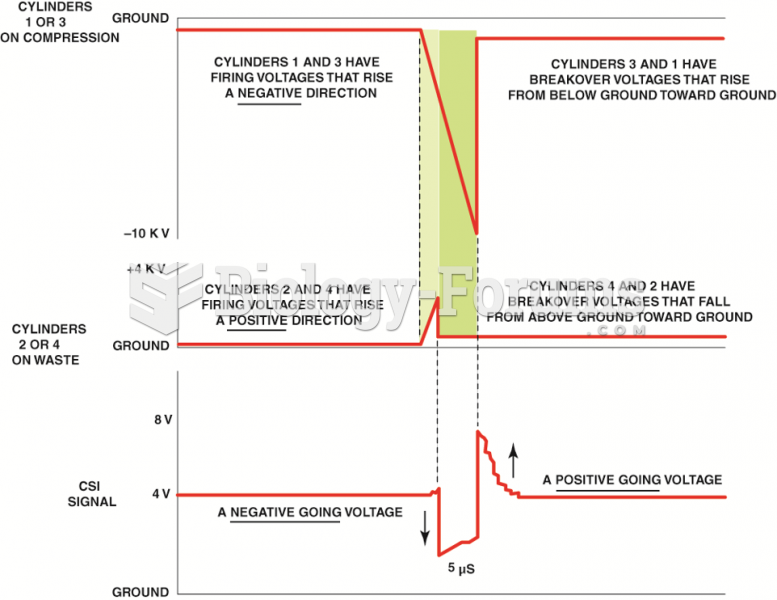 The slight (5 microsecond) difference in the firing of the companion cylinders is enough time to ...
The slight (5 microsecond) difference in the firing of the companion cylinders is enough time to ...