|
|
|
Before a vaccine is licensed in the USA, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reviews it for safety and effectiveness. The CDC then reviews all studies again, as well as the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Academy of Family Physicians. Every lot of vaccine is tested before administration to the public, and the FDA regularly inspects vaccine manufacturers' facilities.
Signs of depression include feeling sad most of the time for 2 weeks or longer; loss of interest in things normally enjoyed; lack of energy; sleep and appetite disturbances; weight changes; feelings of hopelessness, helplessness, or worthlessness; an inability to make decisions; and thoughts of death and suicide.
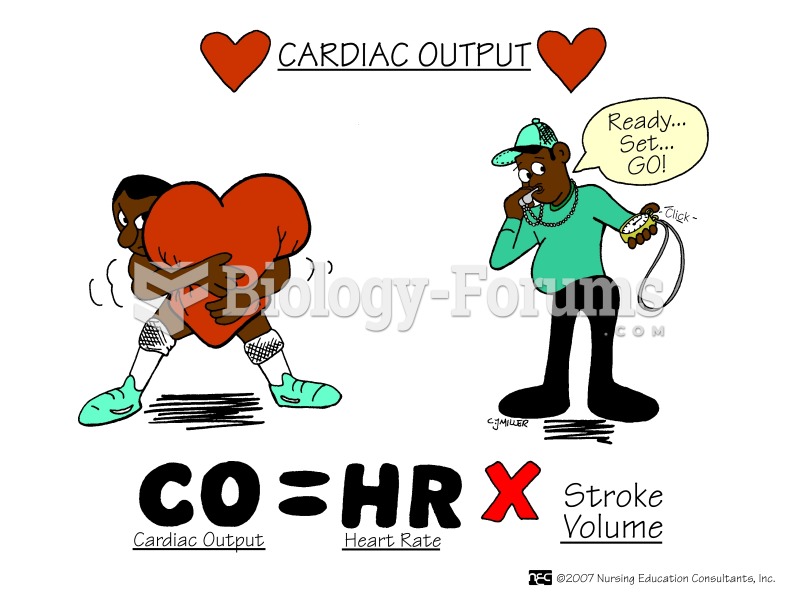
Your heart beats over 36 million times a year.
The first successful kidney transplant was performed in 1954 and occurred in Boston. A kidney from an identical twin was transplanted into his dying brother's body and was not rejected because it did not appear foreign to his body.
A recent study has found that following a diet rich in berries may slow down the aging process of the brain. This diet apparently helps to keep dopamine levels much higher than are seen in normal individuals who do not eat berries as a regular part of their diet as they enter their later years.