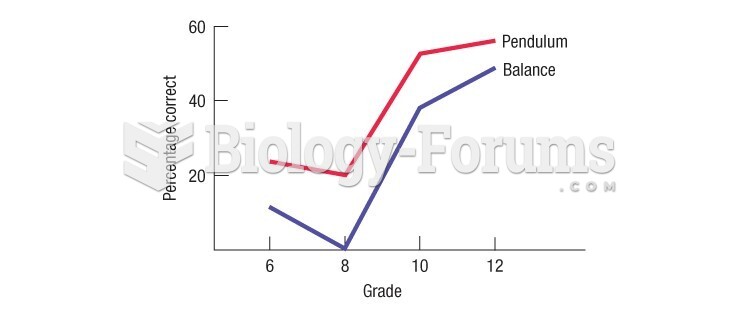
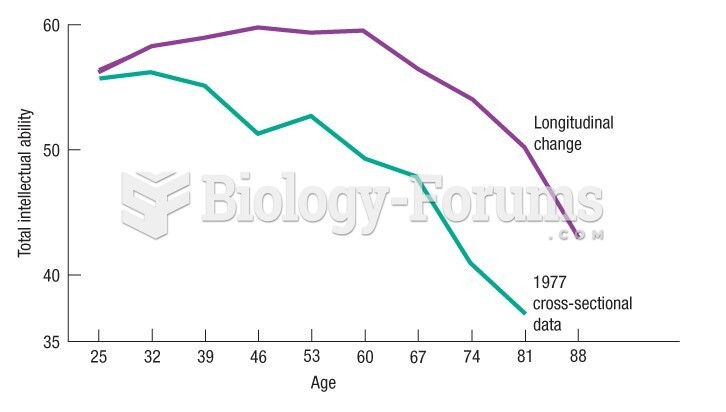
|
|
|
Intradermal injections are somewhat difficult to correctly administer because the skin layers are so thin that it is easy to accidentally punch through to the deeper subcutaneous layer.
The highest suicide rate in the United States is among people ages 65 years and older. Almost 15% of people in this age group commit suicide every year.
Sperm cells are so tiny that 400 to 500 million (400,000,000–500,000,000) of them fit onto 1 tsp.
All adverse reactions are commonly charted in red ink in the patient's record and usually are noted on the front of the chart. Failure to follow correct documentation procedures may result in malpractice lawsuits.
The heart is located in the center of the chest, with part of it tipped slightly so that it taps against the left side of the chest.