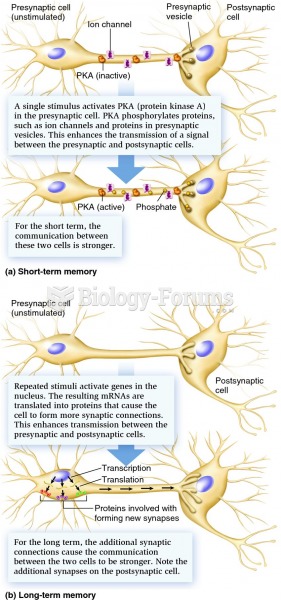
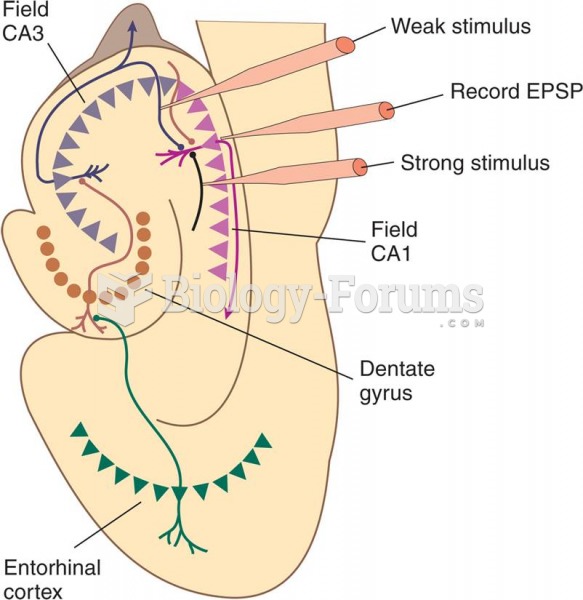
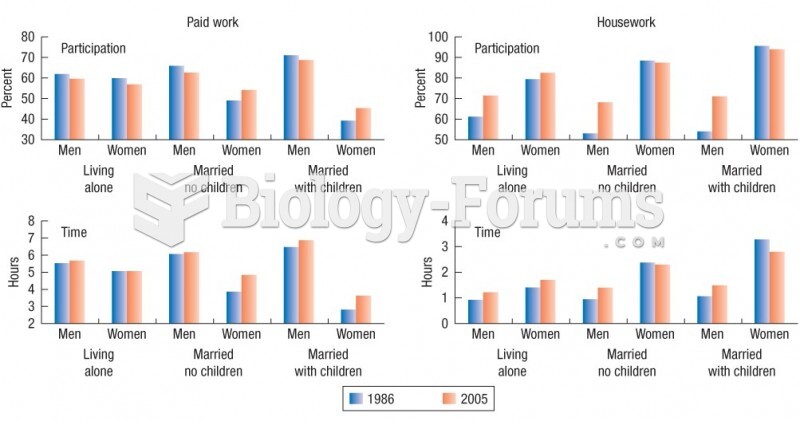
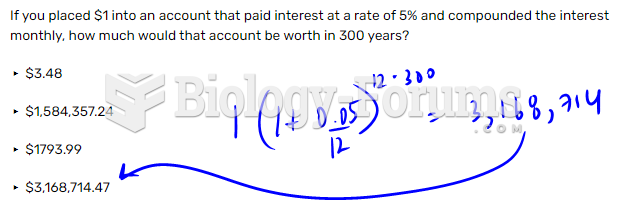|
|
|
Blood is approximately twice as thick as water because of the cells and other components found in it.
Critical care patients are twice as likely to receive the wrong medication. Of these errors, 20% are life-threatening, and 42% require additional life-sustaining treatments.
Elderly adults are at greatest risk of stroke and myocardial infarction and have the most to gain from prophylaxis. Patients ages 60 to 80 years with blood pressures above 160/90 mm Hg should benefit from antihypertensive treatment.
The B-complex vitamins and vitamin C are not stored in the body and must be replaced each day.
All adverse reactions are commonly charted in red ink in the patient's record and usually are noted on the front of the chart. Failure to follow correct documentation procedures may result in malpractice lawsuits.