Answer to Question 1
Some of the major causes of cognitive disability are as follows:
Toxemia: Toxic (poisonous) substances in the blood during the gestation period pose a risk for both the pregnant woman and the fetus. Such substances include prescription drugs, cocaine and other illegal drugs, nicotine (from smoking), and alcohol. A toxic disorder that has received considerable publicity is fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS). It is associated with heavy drinking (generally considered to be five or six drinks on occasion) during the gestation period. Pregnant women who occasionally have one or two drinks also place their fetus at some risk for FAS, which is characterized by facial and cranial abnormalities, possible heart defects, delayed physical and intellectual development, joint and limb anomalies, decreased weight of the fetus, and increased risk of stillbirth. The risk of toxemia can be substantially reduced if pregnant women receive early, regular, and specialized care during pregnancy.
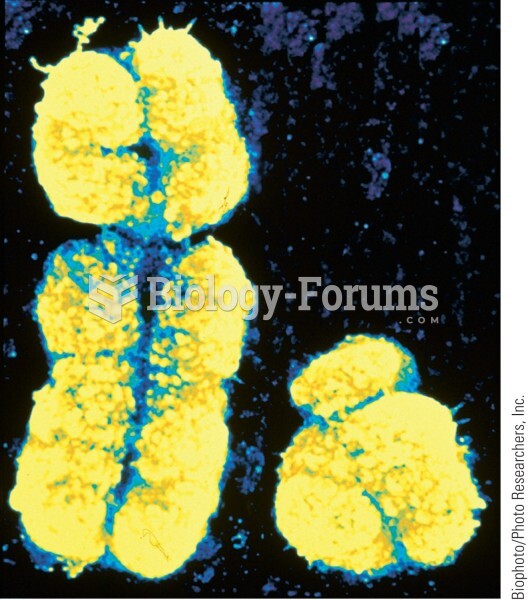
Chromosome abnormalities: The best-known and most common disorder in this category is Down syndrome. This condition arises because there are 47 chromosomes, rather than the usual 46, in the cells of those affected. The disorder does not appear to be inherited, although the reason for this chromosome abnormality is not known. Down syndrome children and adults generally experience a moderate to severe level of cognitive disability. Many of those affected also have physical anomalies, which may include heart lesions and gastrointestinal difficulties. There are a variety of other chromosomal abnormalities that may occur. Fragile X syndrome is the most common inherited form of cognitive disability. Symptoms of fragile X syndrome can range from mild learning disability to a severe level of cognitive disability, with serious behavioral problems. Some carriers are completely normal but can pass the gene that produces the syndrome to later generations. Fragile X syndrome is incurable.
Metabolic disorders: Phenylketonuria (PKU) is perhaps the best-known metabolic disease. The affected infant cannot metabolize phenylalanine, an essential building block of protein in food. As a result, phenylalanine and its derivative, phenyl pyruvic acid, build up in the body and rapidly poison the central nervous system, causing irreversible brain damage. About a third of such children cannot walk, about two-thirds never learn to talk, and more than half have a profound level of cognitive disability. PKU results from the action of a recessive gene that is inherited from each parent. Affected babies can be identified by a simple test of the urine about 3 weeks after birth. Once identified, the infants can be placed on a diet that controls the level of phenylalanine in their system until age 6, at which time the brain is nearly fully developed and their chances of surviving with normal intelligence and health are good. Lipid storage disorders include Tay-Sachs disease, Hunter's disease, and Hurler's syndrome. These disorders involve a progressive degenerative process due to the accumulation of fatty substances in the cells that eventually leads to the death of the affected individuals. These conditions are inherited, and as yet effective treatment has not been developed.
Answer to Question 2
b