|
|
|
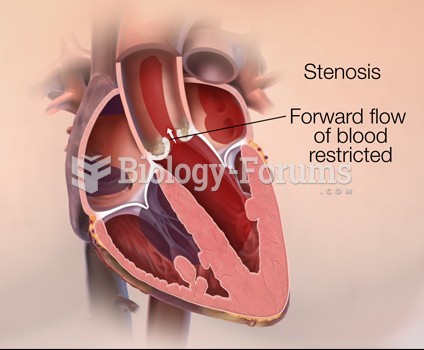
Nitroglycerin is used to alleviate various heart-related conditions, and it is also the chief component of dynamite (but mixed in a solid clay base to stabilize it).
The strongest synthetic topical retinoid drug available, tazarotene, is used to treat sun-damaged skin, acne, and psoriasis.
The cure for trichomoniasis is easy as long as the patient does not drink alcoholic beverages for 24 hours. Just a single dose of medication is needed to rid the body of the disease. However, without proper precautions, an individual may contract the disease repeatedly. In fact, most people develop trichomoniasis again within three months of their last treatment.
Of the estimated 2 million heroin users in the United States, 600,000–800,000 are considered hardcore addicts. Heroin addiction is considered to be one of the hardest addictions to recover from.
After a vasectomy, it takes about 12 ejaculations to clear out sperm that were already beyond the blocked area.