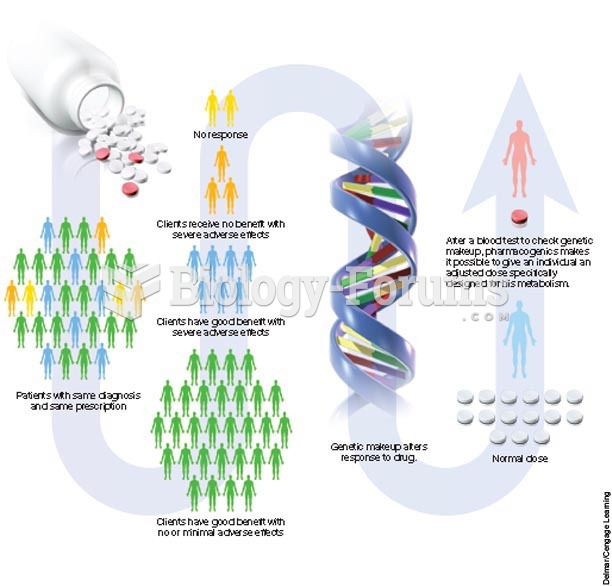
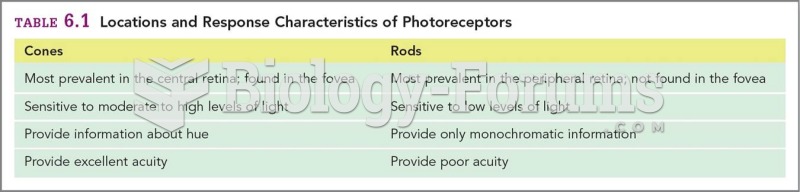
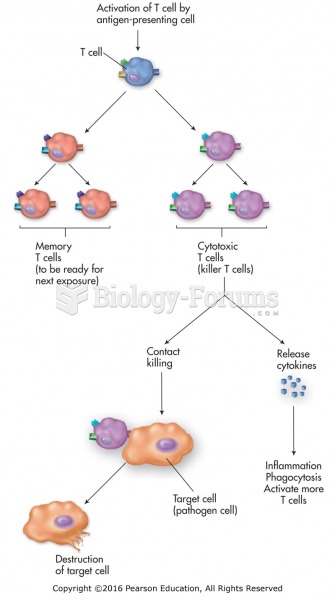
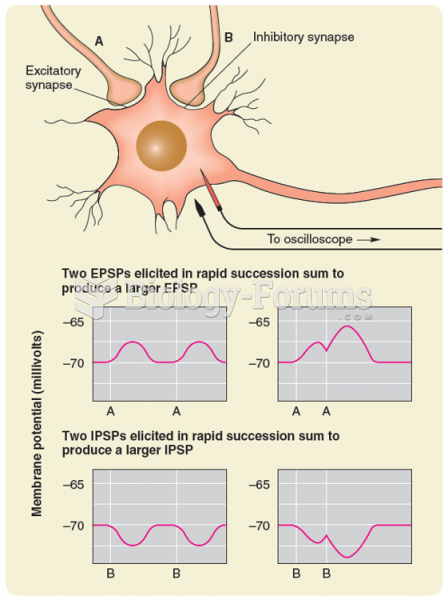
|
|
|
Normal urine is sterile. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products. It is free of bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
IgA antibodies protect body surfaces exposed to outside foreign substances. IgG antibodies are found in all body fluids. IgM antibodies are the first type of antibody made in response to an infection. IgE antibody levels are often high in people with allergies. IgD antibodies are found in tissues lining the abdomen and chest.
Drug abusers experience the following scenario: The pleasure given by their drug (or drugs) of choice is so strong that it is difficult to eradicate even after years of staying away from the substances involved. Certain triggers may cause a drug abuser to relapse. Research shows that long-term drug abuse results in significant changes in brain function that persist long after an individual stops using drugs. It is most important to realize that the same is true of not just illegal substances but alcohol and tobacco as well.
Adults are resistant to the bacterium that causes Botulism. These bacteria thrive in honey – therefore, honey should never be given to infants since their immune systems are not yet resistant.
The modern decimal position system was the invention of the Hindus (around 800 AD), involving the placing of numerals to indicate their value (units, tens, hundreds, and so on).